9 Motor Pathways 1 General Organisation Biology Diagrams The neural pathways in the motor system are like a complex road network, each route serving a specific purpose. The corticospinal tract is the superhighway of voluntary movement. It carries signals directly from the motor cortex to the spinal cord, controlling the muscles of the limbs and trunk. where the limitations of the human body can

The image shows the areas of motor cortex concerned with motor functions in different areas of the body, and much more cortex is used to control muscles that are involved in fine movements. While the executive pathway for control of muscles begins in the motor cortex, many cortico-spinal neurones originate in areas in front and behind the pre The motor system is the set of central and peripheral structures in the nervous system that support motor functions, i.e. movement. [1] [2] Peripheral structures may include skeletal muscles and neural connections with muscle tissues. [2]Central structures include cerebral cortex, brainstem, spinal cord, pyramidal system including the upper motor neurons, extrapyramidal system, cerebellum, and

Anatomy - Lumen Learning Biology Diagrams
The human body is constantly responding to external stimuli within the immediate environment. Perception of and response to these impulses depend on the body's ability to detect these forces and generate an appropriate reply. The ascending and descending pathways of the spinal cord act as a bridge between the external environment and the brain.
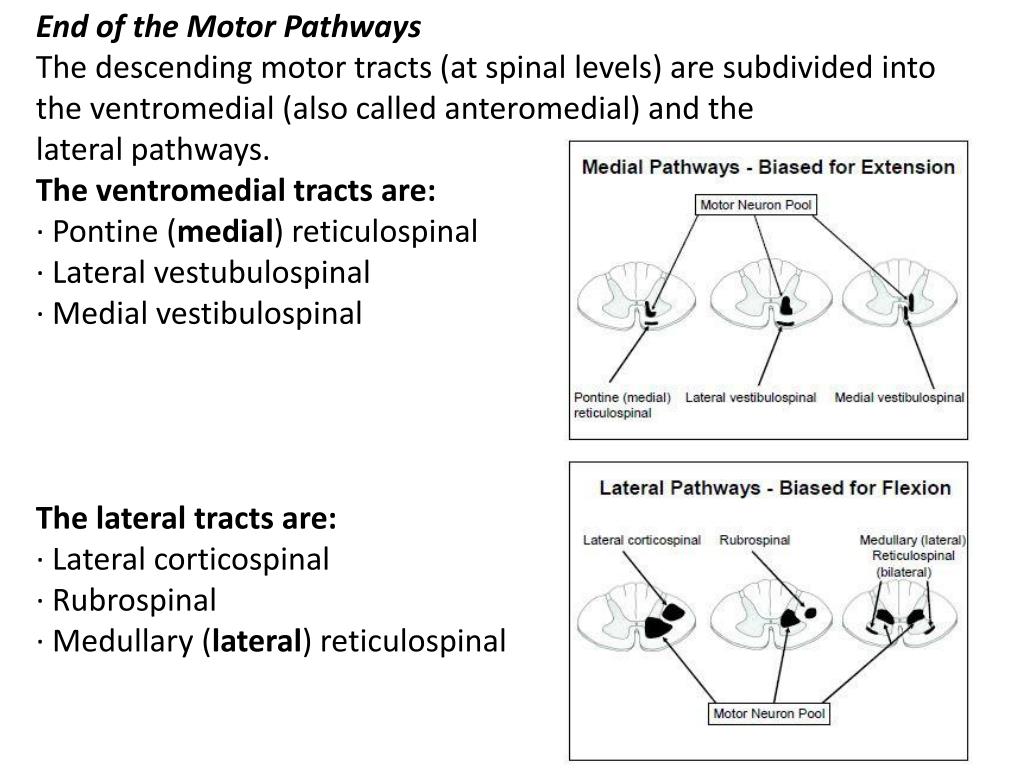
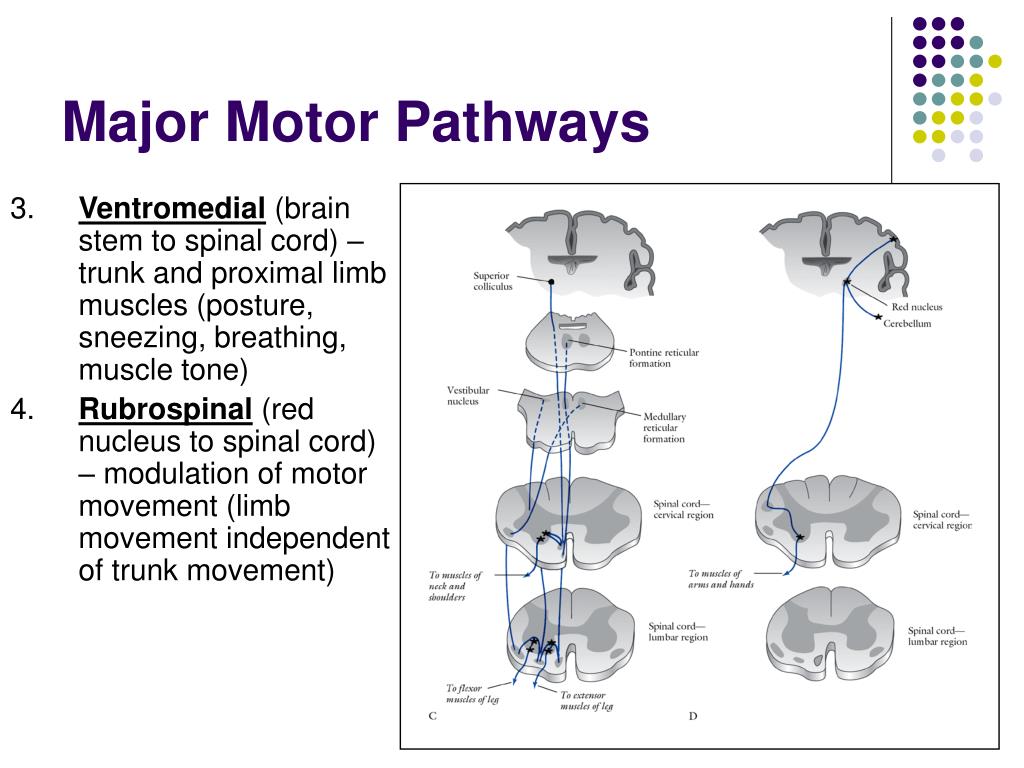
Descending Pathways. The motor output from the cortex descends into the brain stem and to the spinal cord to control the musculature through motor neurons. The upper motor neuron has its cell body in the primary motor cortex of the frontal lobe and synapses on the lower motor neuron, which is in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and Overview of Motor Pathways. Motor pathways are essential networks within the nervous system that are responsible for the transmission of signals from the brain to various muscles throughout the body. They enable voluntary and involuntary movements by coordinating muscle contractions. Understanding these pathways is crucial for comprehending how the body executes movement and maintains balance.
Somatic Motor - Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology ... Biology Diagrams
Betz cells are the largest neurons in the human body, and at 0.1 mm across, the cell bodies are visible to the naked eye in stained tissue. Accordingly, these cells have axons that are among the largest (and fastest) in the human body. Just as the pathway from primary motor cortex to spinal cord is called the pyramidal motor system, the

An Introduction to the Human Body. 1.0 Introduction. 1.1 How Structure Determines Function. 1.2 Structural Organization of the Human Body. 1.3 Homeostasis. 1.4 Anatomical Terminology. All of these motor pathways project to the spinal cord to synapse with motor neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. These lower motor neurons are the The motor pathway, also called the pyramidal tract or the corticospinal tract, serves as the motor pathway for upper motor neuronal signals coming from the cerebral cortex and from primitive brainstem motor nuclei. whereas Huntington's disease is characterized by an inability to prevent parts of the body from moving unintentionally. It is

