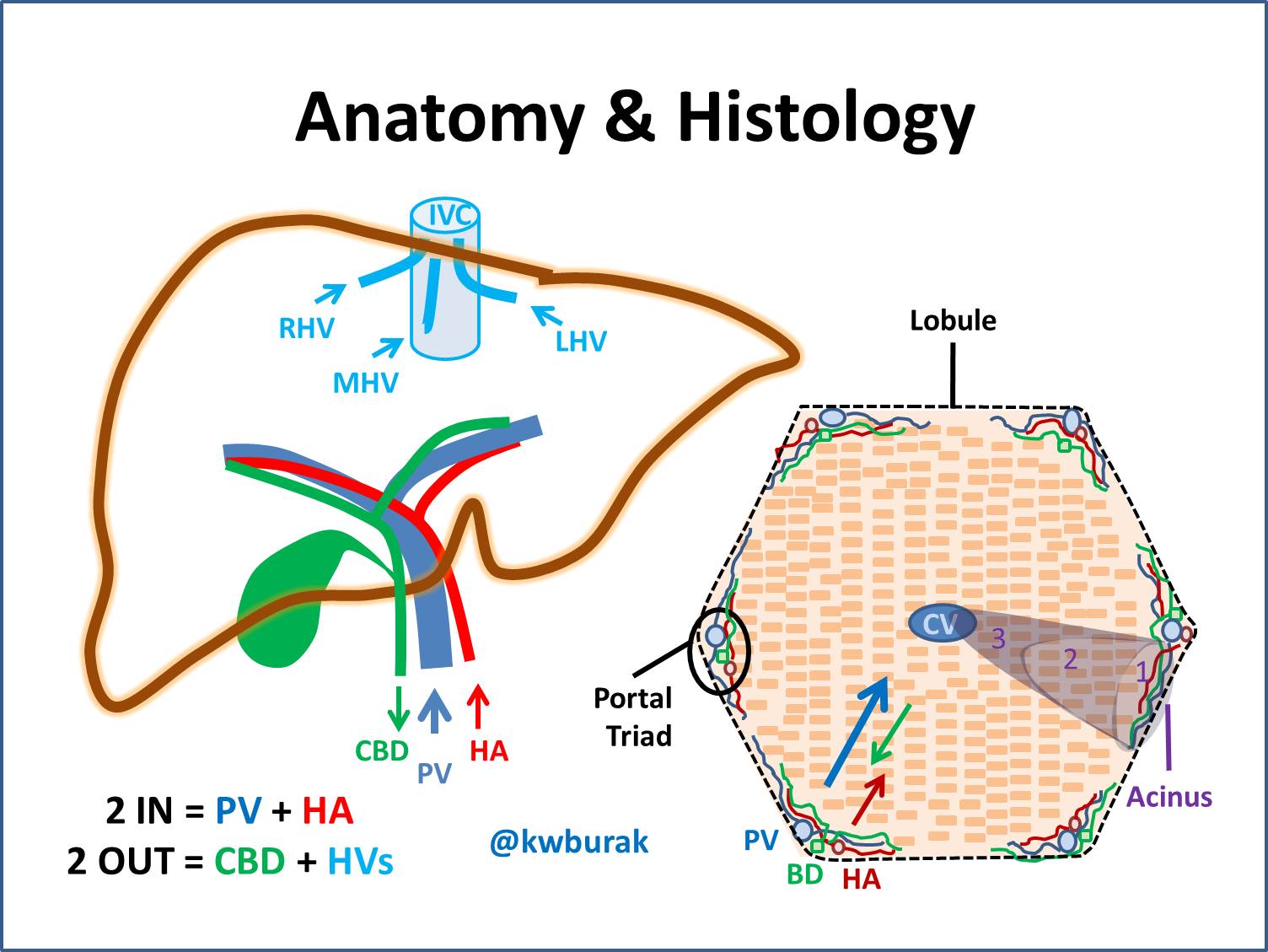
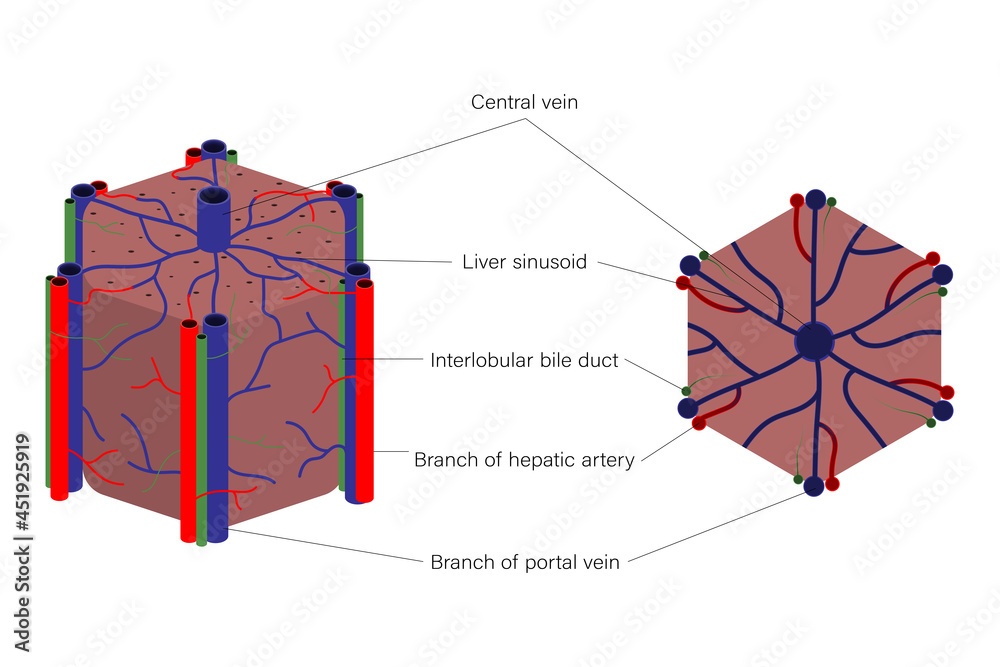
A level biology Structure of the liver lobule Diagram Biology Diagrams In histology (microscopic anatomy), the lobules of liver, or hepatic lobules, are small divisions of the liver defined at the microscopic scale. The hepatic lobule is a building block of the liver tissue, consisting of portal triads, hepatocytes arranged in linear cords between a capillary network, and a central vein.. Lobules are different from the lobes of liver: they are the smaller Liver Anatomy). The quadrate lobe is located on the inferior surface of the right lobe. The caudate lobe is located between the left and right lobes in an anterior and superior location. The liver is the largest gland in the body and is ideally located to receive absorbed nutrients and detoxify absorbed drugs and other noxious substances.

Portal area - situated at he corner of each lobule, it is a complex composed of branches of the hepatic portal vein, hepatic artery, bile duct, and nerve. Bile ducts - any of the ducts that convey bile from the liver. Bile is drained from the liver cells by many small ducts that unite to form the main bile duct of the liver, the hepatic duct. The liver is a peritoneal organ positioned in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. It is the largest visceral structure in the abdominal cavity, and the largest gland in the human body. An accessory digestion gland, the liver performs a wide range of functions, such as synthesis of bile, glycogen storage and clotting factor production.. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the Lobes of the Liver 1. Right Lobe. The liver's right lobe is significantly larger than the left. It occupies most of the right upper abdomen (right hypochondrium). The ligamentum venosum marks its upper boundary, while the round ligament (ligamentum teres hepatis) defines the lower edge.

Lobules of liver Biology Diagrams
The complexities and nuances of liver anatomy require continual respect and lifelong learning by liver surgeons. REFERENCES. 1. Ishizaki M, Nemoto M, et al. Close relation between the inferior vena cava ligament and the caudate lobe in the human liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2007;14(3):297-301. doi: 10.1007/s00534-006-1148-7. The lobules of liver (lobuli hepatis) form the chief mass of the hepatic substance; they may be seen either on the surface of the organ, or by making a section through the gland, as small granular bodies, about the size of a millet-seed, measuring from 1 to 2.5 mm. in diameter. In the human subject their outlines are very irregular; but in some of the lower animals (for example, the pig) they

Liver anatomy Author: Alexandra Sieroslawska, MD • Reviewer: Dimitrios Mytilinaios, MD, PhD Last reviewed: October 30, 2023 which are further divided into even smaller segments in accordance with the blood supply of the liver. The right lobe is the largest of the four lobes and the left lobe is a flattened smaller one. These two lobes are
Anatomy of the Liver Biology Diagrams
In human anatomy, the liver is divided grossly into four parts or lobes: the right lobe, the left lobe, the caudate lobe, and the quadrate lobe.Seen from the front - the diaphragmatic surface - the liver is divided into two lobes: the right lobe and the left lobe. Viewed from the underside - the visceral surface - the other two smaller lobes, the caudate lobe and the quadrate lobe, are