Abdominopelvic Cavity Diagram Biology Diagrams The abdominal cavity is the largest hollow space in the human body, containing many vital organs involved in digestion, excretion, and other essential functions. It is lined by a protective membrane called the peritoneum and houses organs such as the stomach, liver, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, intestines, and various blood vessels and nerves. Major Organs in the Four Quadrants. Here are some of the major organs that you'll find in each of the four abdominal quadrants: Right Upper Quadrant: Liver, stomach, gallbladder, duodenum, right kidney, pancreas, and the right adrenal gland.; Left Upper Quadrant: Liver, stomach, pancreas, left kidney, spleen, and the left adrenal gland.; Right Lower Quadrant: appendix, reproductive organs Abdominal Body Cavity: Labeled diagram of the abdominal cavity showing the small intestine (brown) covered by the visceral peritoneum (inner green layer), and the parietal peritoneum (outer red layer) lining the abdominal cavity. The peritoneal cavity is the potential space between the visceral and parietal peritoneum and contains peritoneal fluid.
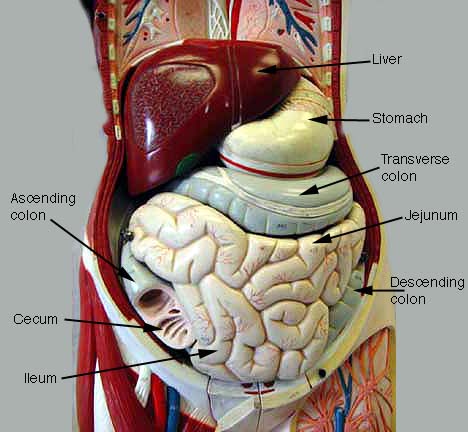
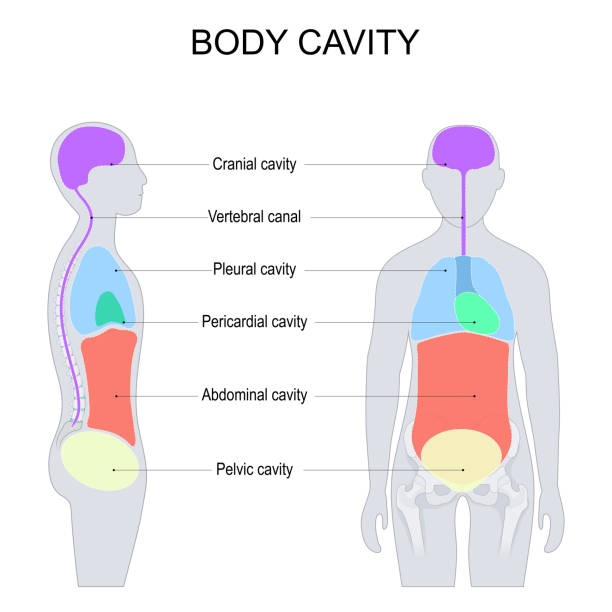
GI Tract Peritoneal Cavity Kidney and Ureter Anterior Abdominal Wall Posterior Abdominal Wall and Retroperitoneum Pelvic Floor and Perineum Nerves of the Abdomen and Pelvis Abdomen and Pelvis Blood Supply Male Reproductive System Female Reproductive System Liver Gallbladder and Biliary Tract Pancreas Spleen Bladder, Prostate and Urethra Learn about the abdominal cavity, a large space in the torso that contains digestive, reproductive, and excretion organs. See a diagram of the abdominal cavity and its regions, and test your knowledge with a quiz. The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans [1] and many other animals that contain organs.It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. [2] It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity.Its dome-shaped roof is the thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle under the lungs, and its floor is the pelvic inlet, opening into the pelvis.

Definition and Organs Biology Diagrams
The abdominal cavity is the part of the body that houses the stomach, liver, pancreas, kidneys, gallbladder, spleen, and the large and small intestines. The diaphragm marks the top of the abdomen and the horizontal line at the level of the top of the pelvis marks the bottom. Connective tissue called the mesentery holds the abdominal organs abdominal cavity, largest hollow space of the body. Its upper boundary is the diaphragm, a sheet of muscle and connective tissue that separates it from the chest cavity; its lower boundary is the upper plane of the pelvic cavity. Vertically it is enclosed by the vertebral column and the abdominal and other muscles. The abdominal cavity contains the greater part of the digestive tract, the The abdomen is a vital anatomical region that houses major organs involved in digestion, excretion, and other essential bodily functions. The abdominal cavity is bordered by the diaphragm superiorly and the pelvic inlet inferiorly. Detailed 3D models provide comprehensive insights into the anatomical structures and their relationships
Full labeled anatomical diagrams - Anatomy of the abdomen and digestive system: these general diagrams show the digestive system, with the major human anatomical structures labeled (mouth, tongue, oral cavity, teeth, buccal glands, throat, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gallbladder and pancreas).

