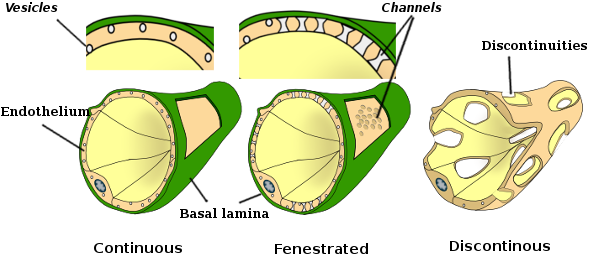
Amandas A to Z Medical Pocket Books Biology Diagrams The first hint of endothelial cell heterogeneity, a structural heterogeneity, was obtained following electron microscopy observations where differences in intercellular junctions led to the classification of continuous endothelium, fenestrated endothelium and discontinuous endothelium [92]. Continuous endothelium is found in most arteries, veins and capillaries of the brain, skin, lung, heart The vascular endothelium is the inner-most structure that coats the interior walls of arteries, capillaries and veins. Endothelial cells (EC) were described to anchor to an 80-nm-thick basal lamina (BL). Both EC and BL constitute the vascular intima, establishing a hemocompatible surface,

The endothelium is a thin layer of single flat cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels.[1]Endothelium is of mesodermal origin. Both blood and lymphatic capillaries are composed of a single layer of endothelial cells called a monolayer. In straight sections of a blood vessel, vascular endothelial cells typically align and elongate in the direction of fluid flow. Continuous capillaries are generally found in the nervous system, as well as in fat and muscle tissue. Within nervous tissue, the continuous endothelial cells form a blood brain barrier, limiting the movement of cells and large molecules between the blood and the interstitial fluid surrounding the brain. Fenestrated

Endothelium Biology Diagrams
Capillary angiosarcoma. Rare cancer of the endothelial cells that can affect the capillaries. Capillary leak syndrome. A condition that causes a sudden drop in blood pressure. It sometimes requires emergency treatment. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. An inherited blood vessel disorder that causes abnormal growths (telangiectases) that

1. Vascular Endothelial Cells. Vascular endothelial cells (VECs) are a type of endothelial cells that cover the inside walls of blood vessels, such as capillaries, veins, and arteries, and act as a protective barrier between the circulating blood and the surrounding tissues.

Vascular endothelial cell development and diversity Biology Diagrams
The blood vessels in our bodies are either arteries, veins or capillaries. Arteries transport blood away from the heart, veins carry it back, and capillaries connect arteries and veins, while also facilitating the exchange of gases and nutrients between the blood and different organs (Augustin and Koh, 2017).The inner layer of every blood vessel is formed by endothelial cells, but what factors
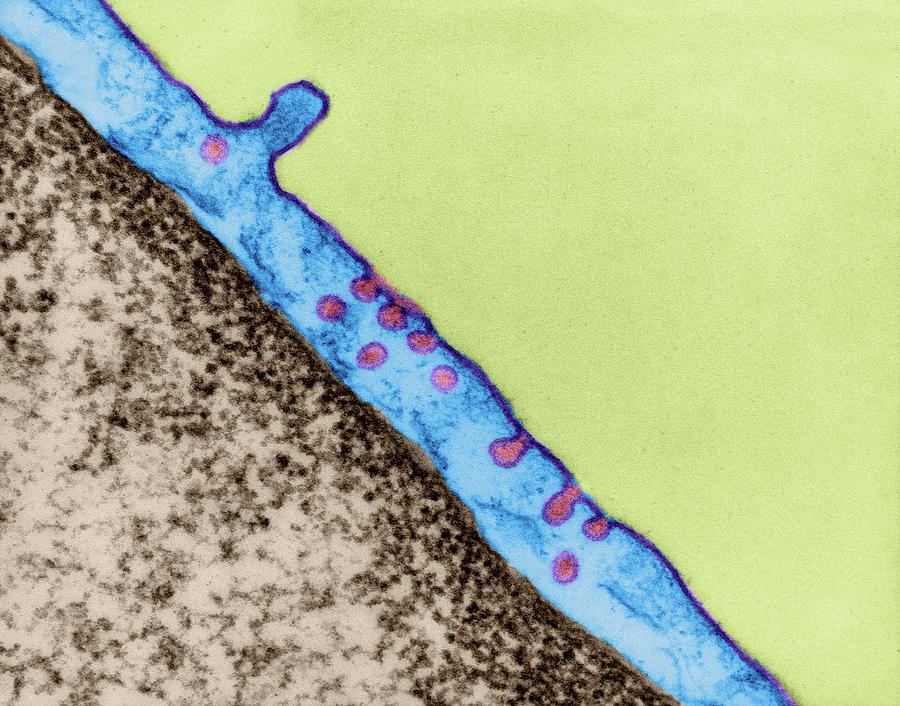
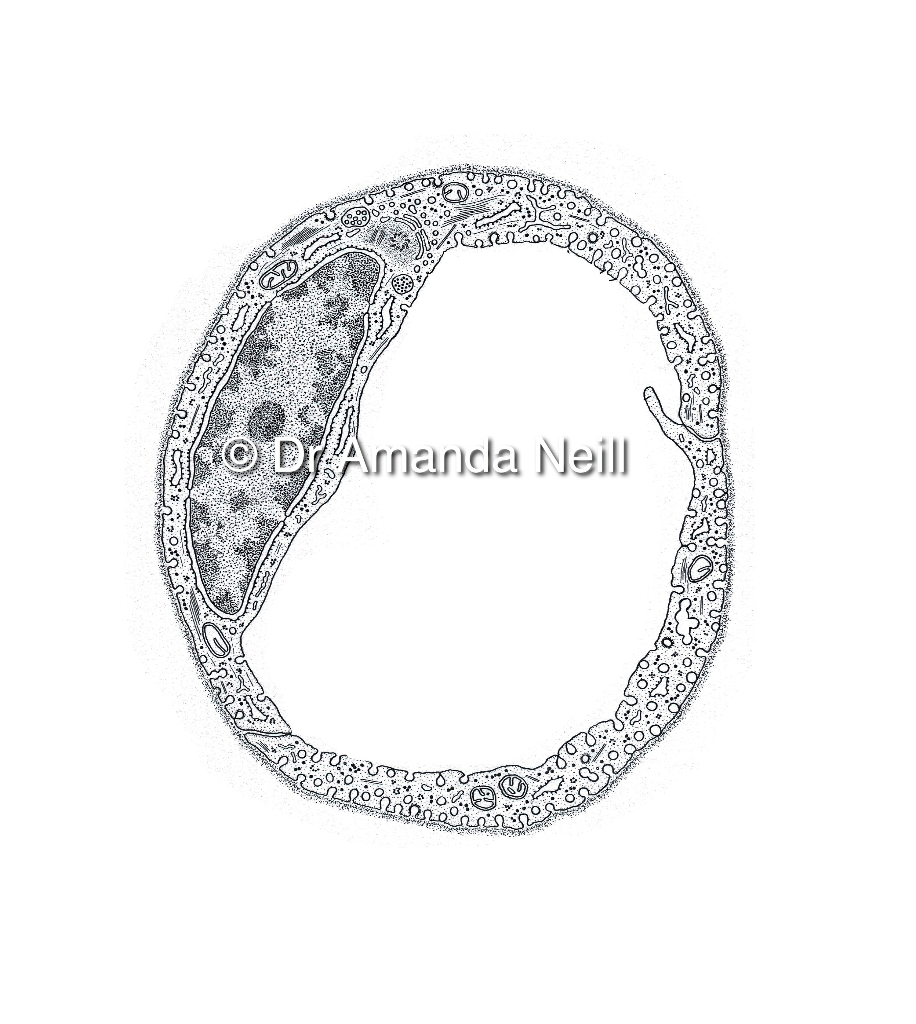
Endothelial Cells Line All Blood Vessels. The largest blood vessels are arteries and veins, which have a thick, tough wall of connective tissue and and many layers of smooth muscle cells (Figure 22-22).The wall is lined by an exceedingly thin single sheet of endothelial cells, the endothelium, separated from the surrounding outer layers by a basal lamina. The endothelium, a monolayer of endothelial cells, constitutes the inner cellular lining of the blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries) and the lymphatic system, and therefore is in direct contact with the blood/lymph and the circulating cells. The term "endothelium" was first coined in 1865 by the Swiss anatomist, Wilhelm His [20,537]. Then, and thereafter up to the early 1970s