Autophagy in Cell Survival and Death Biology Diagrams More importantly, cell cycle inhibitors, such as genotoxic drugs that cause DNA damage and cell cycle arrest to inhibit tumor cell division, always activate autophagy, which delays cell death and may therefore lead to chemoresistance 15, 126, 173. It is important to evaluate the ability of specific autophagy to affect the efficacy and

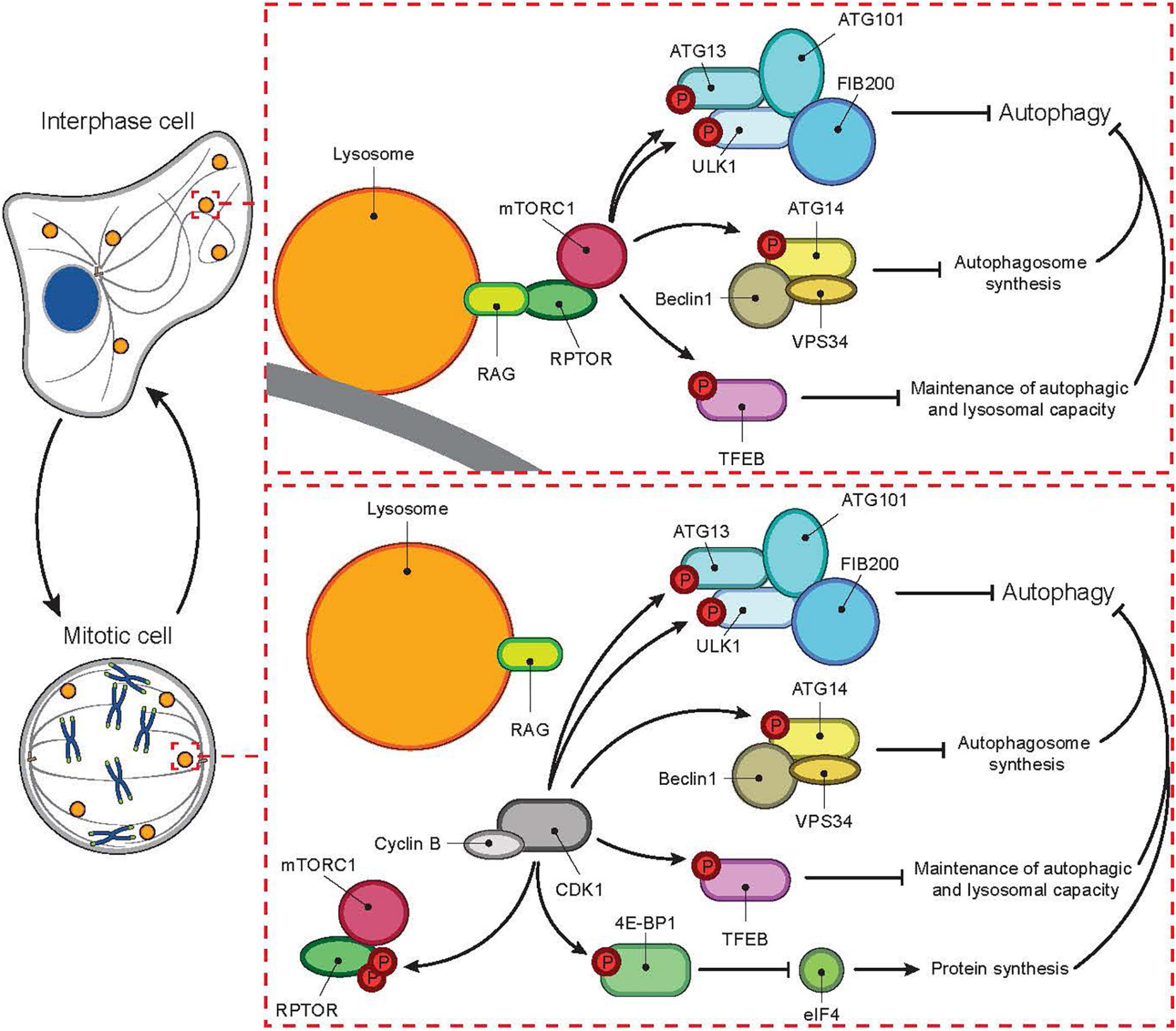
During the progression of the cell cycle, autophagy mostly occurs during interphase, in particular in the G1 and S phases [20,21,22]. Indeed, repression of autophagy during mitosis protects condensed genomes and organelles movements from accidental autophagic engulfment. Hence, there is a required control of autophagy by the cell-cycle regulators. The degradation of cell cycle proteins can facilitate cell cycle exit. The process of autophagy also liberates macromolecules for the newly generated cell to build membranes, synthesize RNA and
Autophagy: Renovation of Cells and Tissues Biology Diagrams
Several cellular processes can interfere with the cell cycle, including autophagy, the catabolic pathway involved in degradation of intracellular constituents in lysosomes. According to the mechanism used to deliver cargo to the lysosome, autophagy can be classified as macroautophagy (MA), microautophagy (MI), or chaperone-mediated autophagy Autophagy has been postulated to prevent tumorigenesis by limiting necrosis and inflammation, inducing cell cycle arrest and preventing genome instability [22,23]. Autophagy has also recently been shown to be required for key aspects of the senescent cell phenotype [ 24 ], which is known to be anti-tumourigenic.
Autophagy, like cell cycle arrest, is induced in response to a variety of stress conditions, where it plays a pivotal role in preserving cellular viability . While the correlative induction of autophagy and cell-cycle arrest has been extensively documented, the molecular mechanisms linking them together are still debated and largely unknown. The mammalian cell cycle is divided into four sequential phases, namely G1 (Gap 1), S (synthesis), G2 (Gap 2), and M (mitosis). However, the mechanism underlying the turnover of Wee1 is not fully understood. Autophagy, a highly conserved cellular process, maintains cellular homeostasis by eliminating intracellular aggregations, damaged
Autophagy in the renewal, differentiation and homeostasis of immune ... Biology Diagrams
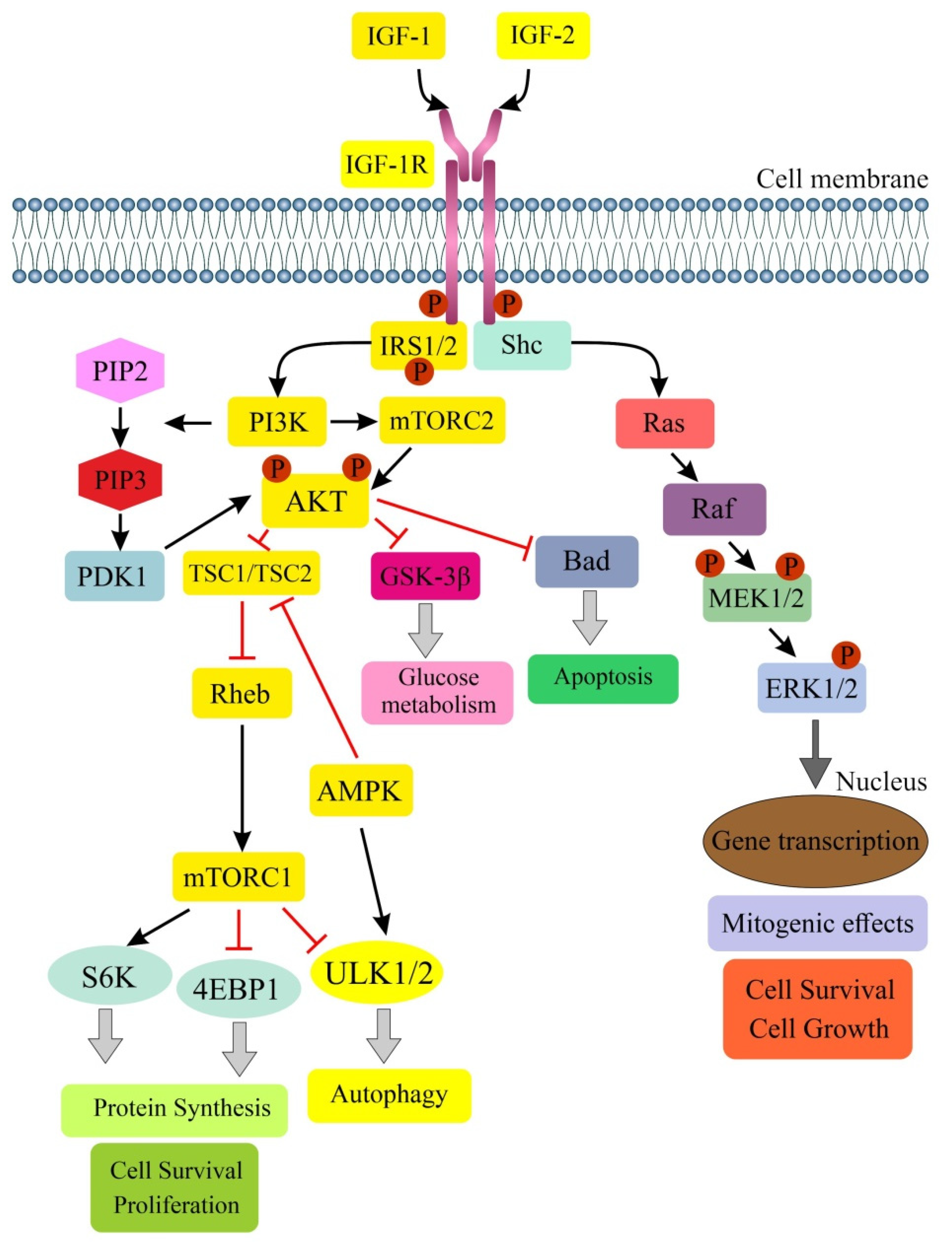
Autophagy is the major intracellular degradation system by which cytoplasmic materials are delivered to and degraded in the lysosome. However, the purpose of autophagy is not the simple elimination of materials, but instead, autophagy serves as a dynamic recycling system that produces new building blocks and energy for cellular renovation and homeostasis. autophagy, is controlled upstream by mTOR (21), which 10, argues for a coordinated regulation of autophagy and cell-cycle progression. In the present review, we will focus on various aspects of the reciprocal regulation connecting autophagy and the cell cycle. Cell-cycle progression is governed by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Autophagy is a self-degradation pathway, in which cytoplasmic material is sequestered in double-membrane vesicles and delivered to the lysosome for degradation. Under basal conditions, autophagy plays a homeostatic function. However, in response to various stresses, the pathway can be further induce …