Biology for NonSTEM Majors Class Notes Biology Diagrams Animal cells vs. Plant cells - Key similarities Animal cells and plant cells are eukaryotic cells. Both animal and plant cells are classified as "Eukaryotic cells," meaning they possess a "true nucleus."Compared to "Prokaryotic cells," such as bacteria or archaea, eukaryotic cells' DNA is enclosed in a membrane-bound nucleus.These membranes are similar to the cell membrane Specialized Organelles: Chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are present in plant and algae cells, but not in animal cells (although various researchers are attempting to create "plantimals" by injecting chloroplasts into the embryonic cells of zebra fish and other species).. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, which is important for photosynthesis. Plants use photosynthesis to derive energy from sunlight.
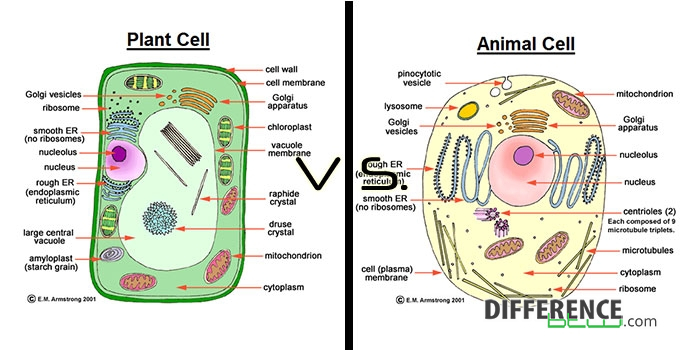
A plant cell is bounded by a cell wall and the living portion of the cell is within the walls and is divided into two portions: the nucleus, or central control center; and the cytoplasm, a fluid in which membrane-bound organelles are found. Between the primary cell walls of adjacent plant cells, lies a pectic middle lamella. There can be a secondary cell wall that would be located just to the The structures possessed by plant cells for performing these two functions create the primary differences between plant and animal cells. Structures Unique to Plant Cells Cell Wall : A wall on the outside of the membrane, which, in combination with the vacuole (as described below), helps the plant cell maintain its shape and rigidity.
Similarities, Differences, Chart, and Examples Biology Diagrams
Plant vs. Animal Cell Size Plant cells are often larger than animal cells. Whereas the size normal range for an animal cell is between 10 and 30 micrometers (µm), plant cells can measure anywhere between 10 and 100 µm.

A plant cell consists of one large vacuole that maintains the shape of the cell and stores nutrients. Animal cells, on the other hand, have multiple smaller vacuoles. Both plant and animal cells have a cell membrane, but only the former has a cell wall. The absence of a wall makes it possible for animals to develop different types of cells and Plant vs Animal Cells: Comparing the Differences. Plant and animals cells contain somewhat different organelles, plus there are distinctions between some that they share in common: Cell Wall. Plant cells are encased in a rigid cell wall composed mainly of cellulose. This wall not only provides structural support but also protects the cell from

Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells Biology Diagrams
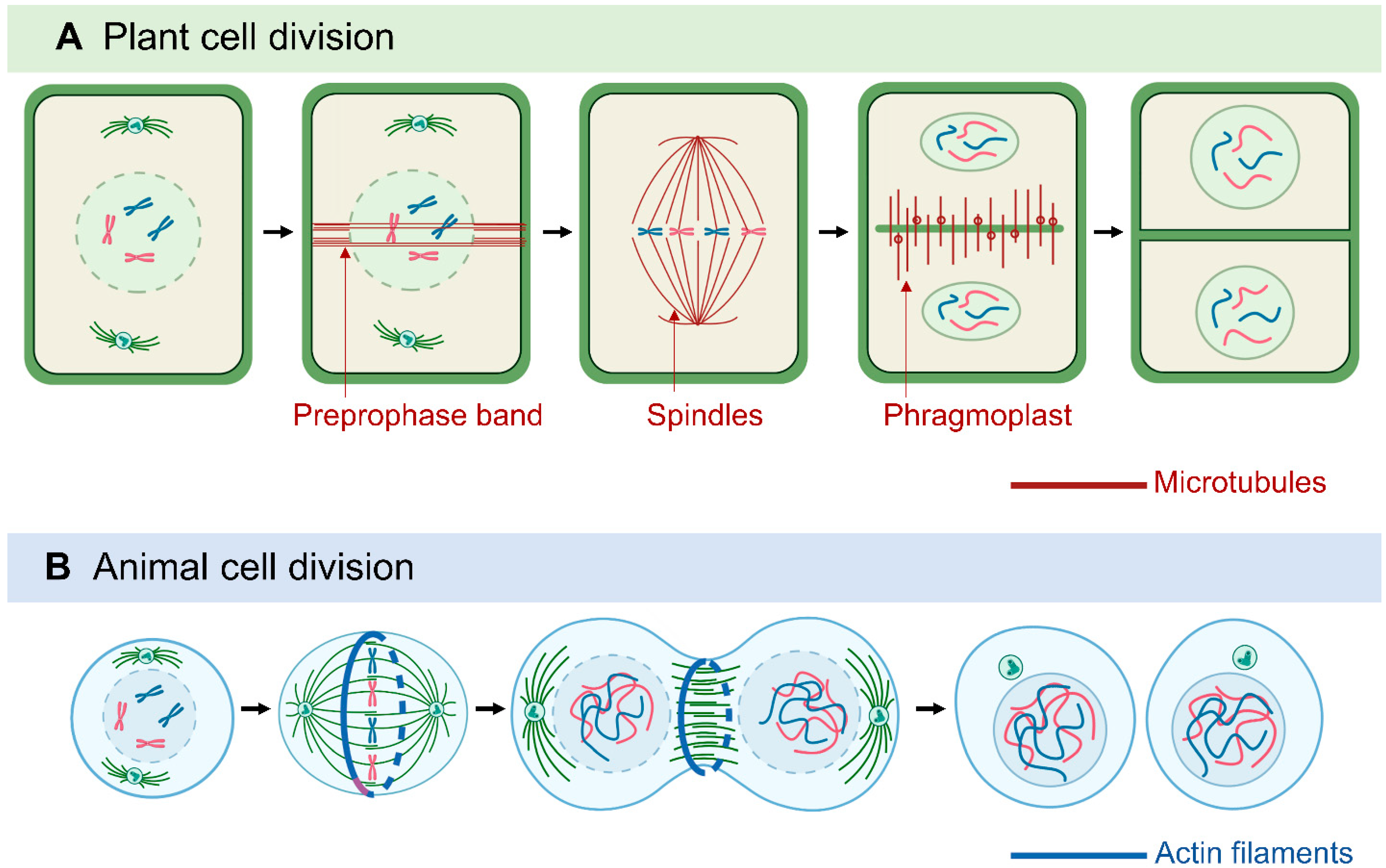
Main Difference - Plant vs Animal Cell Division. Plant and animal cell division occur as a part of their life cycle. Cell division, both in plants and animal cells, can be divided into two types: vegetative cell division and reproductive cell division.The vegetative cell division, which produces genetically identical two daughter cells, is called mitosis. Plant cells are basic functional units of plants constituting all cell organelles performing a variety of functions that support the plants' metabolisms. Size and shape Animal cells are generally smaller than plant cells with their cells ranging from 10-30um in length. When plants and animals reproduce their cells asexually, the process is known as mitosis. Cell division varies between animals and plants, but there are many steps in common. The differences have largely to do with specialized structures in each type of cell. Plants have both a cell membrane and a cell wall, whereas animal cells have no cell wall.

