Cell Cycle Regulation Notes Biology Diagrams The complexity of the regulation of the cell cycle is also reflected in the different alterations leading to aberrant cell proliferation and development of cancer. Consequently, targeting the cell cycle in general and CDK in particular presents unique opportunities for drug discovery. This review provides an overview of deregulation of the cell Learn about the three checkpoints (G1, G2, and M) that control the progression of eukaryotic cell division and the positive and negative regulators of cell cycle. Find out how cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, and other proteins are involved in cell cycle regulation and their roles in DNA damage repair and cancer.

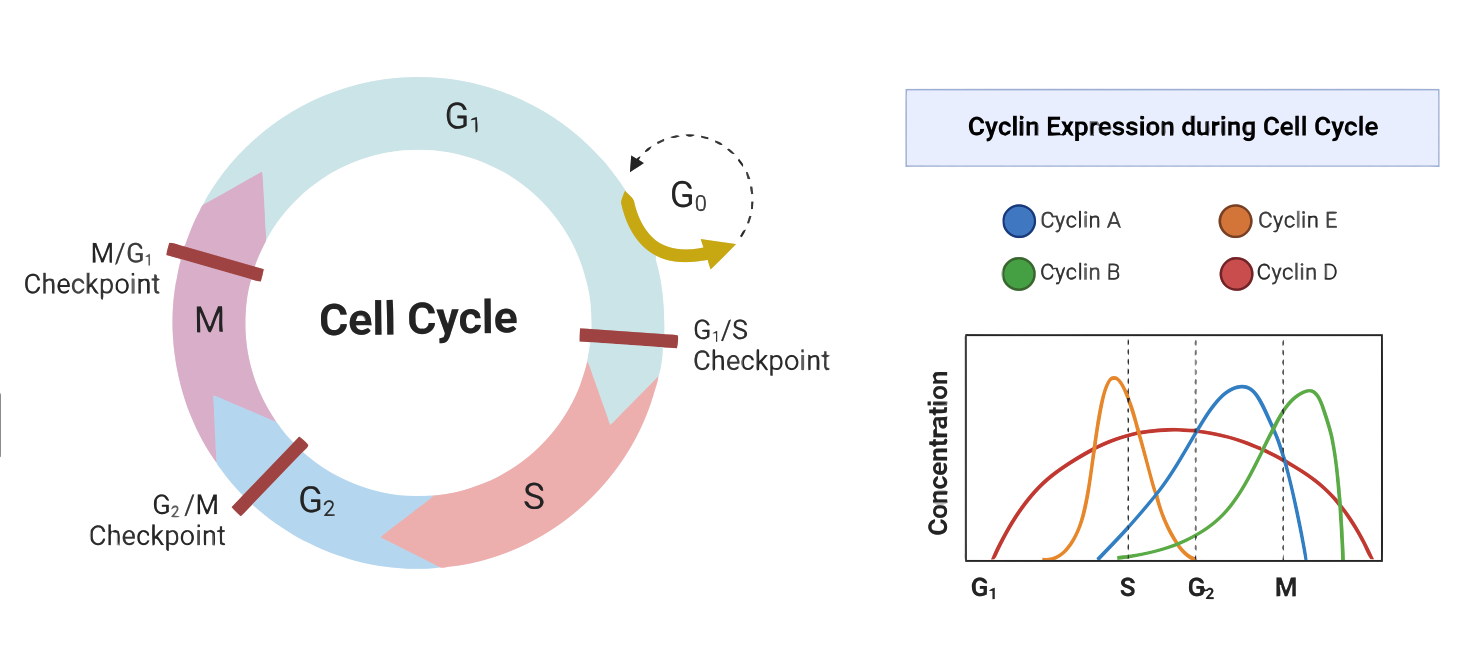
B. Other Cyclins, CDKs and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. Other chemical signals accumulate at different points in the cell cycle. For example, when cells in S are fused with cells in G 1, the G 1 cells begin synthesizing DNA (visualized as 3 H-thymine incorporation). An experiment showing control of progress to different phases of the cell cycle is illustrated below.
The cell cycle: a review of regulation, deregulation and therapeutic ... Biology Diagrams
Learn about the cell cycle, a cycle of stages that cells pass through to divide and produce new cells. Find out the functions, phases, and regulation of the cell cycle, and how it differs for prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Major events of the cell cycle--DNA synthesis, mitosis and cell division-are regulated by a complex network of protein interactions that control the activities of cyclin-dependent kinases. The network can be modeled by a set of nonlinear differential equations and its behavior predicted by numerical … The second approach to understanding cell cycle regulation was the genetic analysis of yeasts, pioneered by Lee Hartwell and his colleagues in the early 1970s.Studying the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, these investigators identified temperature-sensitive mutants that were defective in cell cycle progression.The key characteristic of these mutants (called cdc for cell division cycle

Cell cycle regulation refers to the control mechanisms that determine whether cells will divide, remain dormant, arrest, or undergo programmed cell death. It plays a crucial role in normal tissue repair and regeneration, and its disruption is a key feature of cancer. Various signaling pathways are involved in cell cycle regulation, and A protein called Pom1 localizes to the tips of the cell and halts cell cycle progression via regulation of the Cdr1-Cdr2-Wee1-Cdc2 axis, which is centrally placed in a region called the interphase node. At longer cell lengths, Pom1 can no longer influence this complex, and the cell cycle can progress to M phase [33, 34]. Learn about the cell cycle, the sequence of events that results in cell growth and division. Explore the phases, regulators, and checkpoints of the cell cycle with diagrams and examples.

Cell Cycle Regulation - an overview Biology Diagrams
Negative Regulation of the Cell Cycle. The second group of cell cycle regulatory molecules are negative regulators. Negative regulators halt the cell cycle. Remember that in positive regulation, active molecules cause the cycle to progress. The best understood negative regulatory molecules are retinoblastoma protein (Rb), p53, and p21.