Cell Growth Control Lab Biology Diagrams Cyclin Dependent Kinases (CDKs) are closely connected to the regulation of cell cycle progression, having been first identified as the kinases able to drive cell division. In reality, the human

For example, yeast have only a single CDK, whereas vertebrates have four different ones. As their name suggests, CDKs require the presence of cyclins to become active. Cyclins are a family of The transcriptional cyclin-dependent kinase, CDK7, mediates transcriptional addition to a vital cluster of genes in TNBC, and CDK7 inhibition is a useful therapy for TNBC patients . Thus, different mechanisms exist across various BC subtypes. 4. Targeting CDKs in BC Therapy

Cycle Progression and ... Biology Diagrams
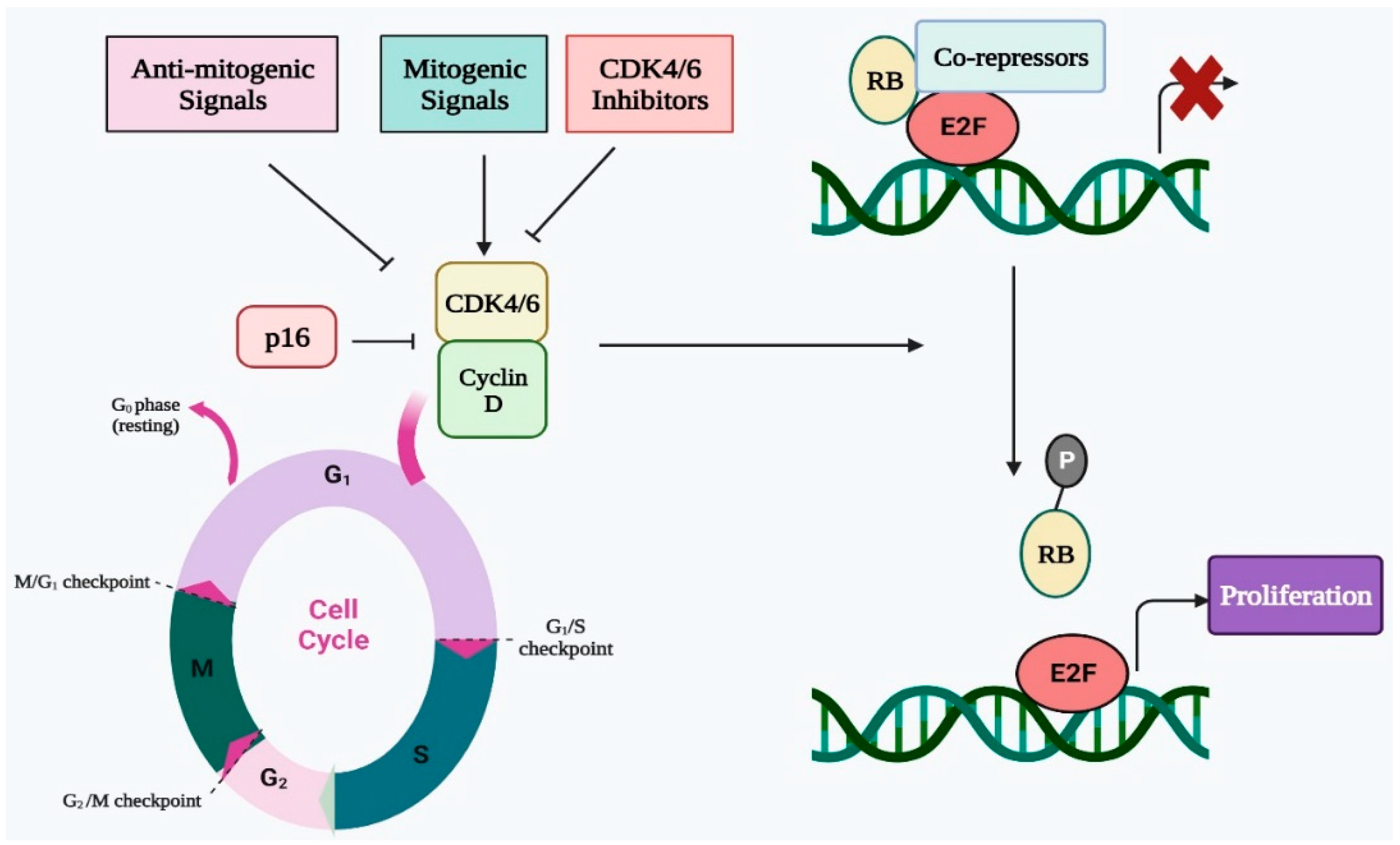
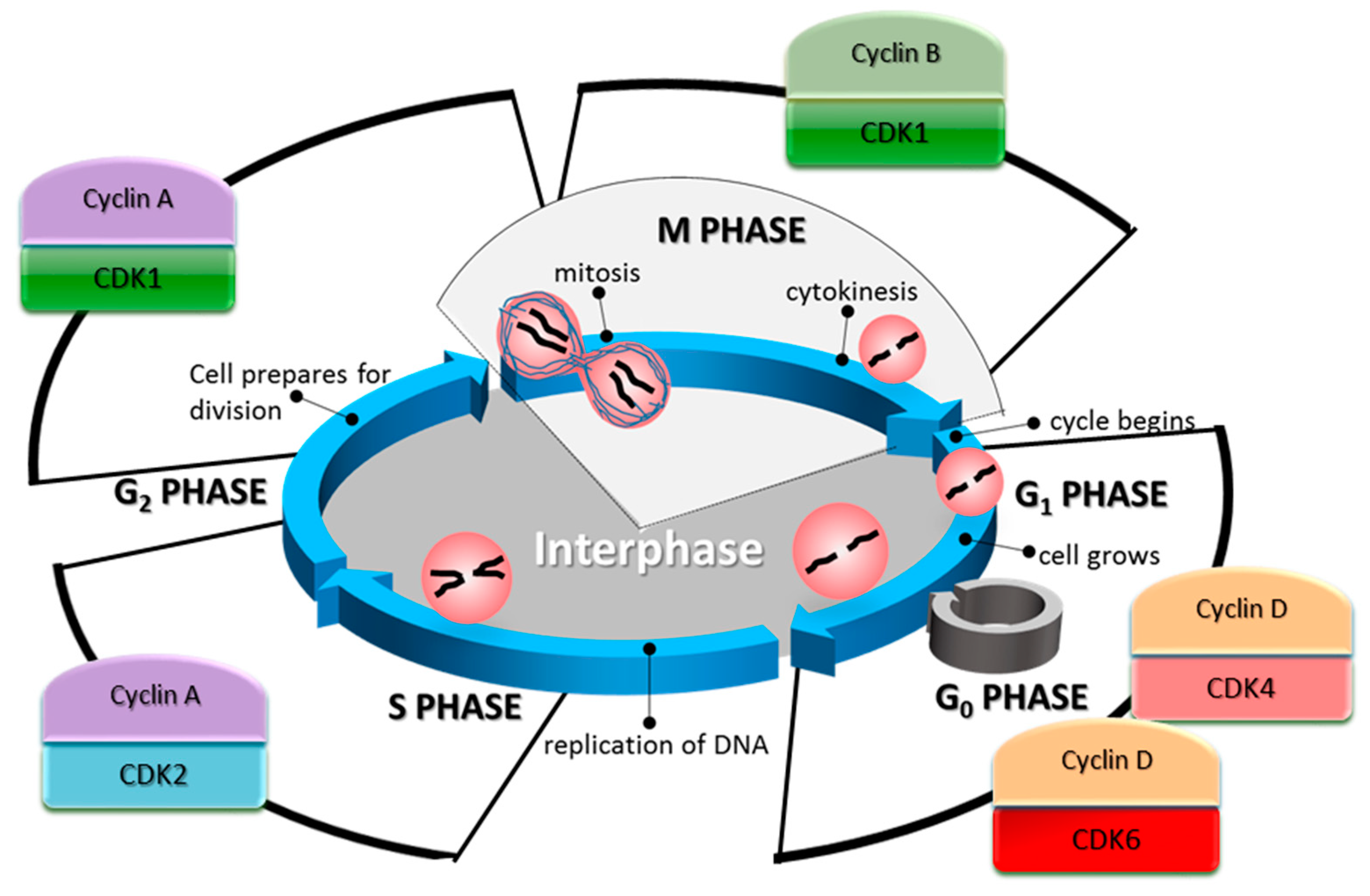
Two groups of proteins, cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks), are responsible for promoting the cell cycle. Cyclins regulate the cell cycle only when they are bound to Cdks; to be fully active, the Cdk/cyclin complex must be phosphorylated, which allows it to phosphorylate other proteins that advance the cell cycle. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Functions. CDKs are serine/threonine kinases that regulate the cell cycle and transcription by phosphorylating specific proteins. Their activity is controlled by cyclins, which bind to CDKs and induce conformational changes that enable substrate recognition and catalytic function. This interaction ensures precise cell The cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), CDK inhibitors (CKIs), and checkpoint proteins are examples of these internal signals that keep an eye on cellular parameters like cell growth, chromosome alignment, and DNA integrity. Protein kinases are the enzymes that activate or inactivate other proteins. They do these by phosphorylation.

Simplified schematic of the regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)5 activity. Involvement of CDK5 in various biological processes. Knowing that CDK5 acts as a major factor during embryonic development of the central nervous system and maintains the entire neurogenesis process during adulthood, the aberrant CDK5 activity result in severe disruptions in synaptic homeostasis.
Cell cycle, Checkpoints, Cyclins and Its Types: Introduction, External ... Biology Diagrams
Defects in cell cycles regulatory machinery is the major reason for many cancers. p53, a tumour suppressor gene is mutated in 75% of all types of cancers and p53 is a CDK inhibitor. In B cell lymphoma G1 cyclin, cyclin D is mutated that lead to unchecked G1S progression. We will discuss the association of cell cycle regulators and cancer later.