Cervical Spine Biology Diagrams Learn about the bony, joint and ligamentous structures of the cervical spine, as well as its movements and functions. The cervical spine consists of seven vertebrae, two groups of joints, and various ligaments that support the head and neck. Learn about the anatomy of the cervical spine, the most superior portion of the vertebral column that supports and cushions the head and neck. Review the features and functions of the cervical vertebrae, discs, facet joints, ligaments and muscles. Learn about the cervical spine, the uppermost section of the vertebral column, consisting of seven vertebrae labeled C1 to C7. It is the most flexible part of the spine, allowing for a wide range of head and neck movements, and protects the spinal cord and nerves.
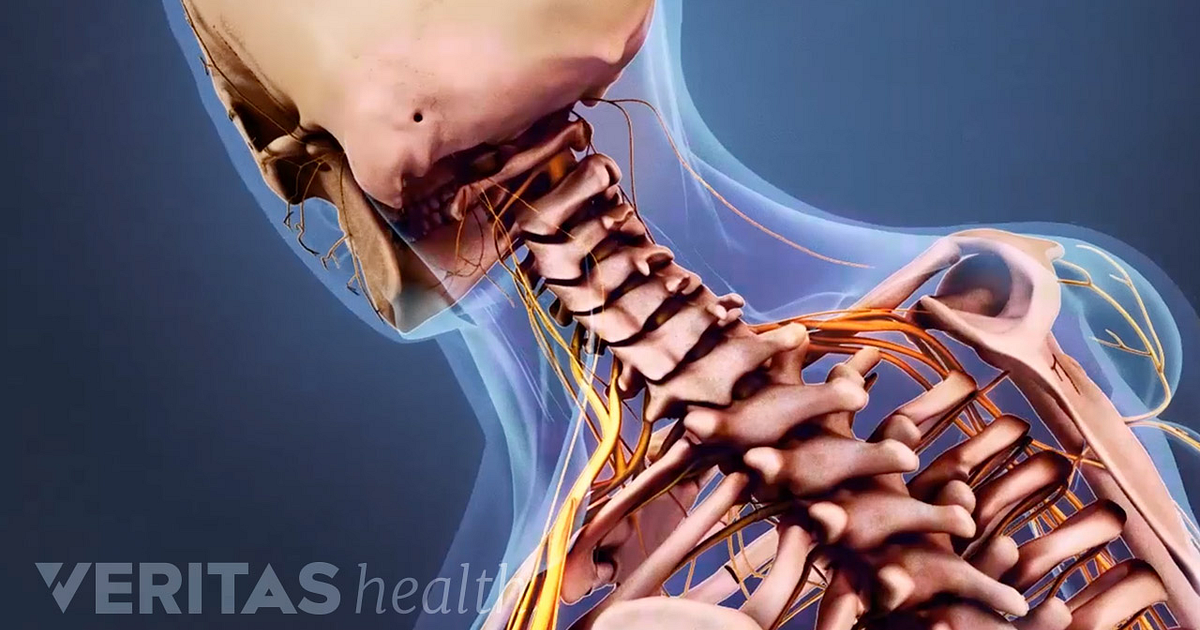
Learn about the bones, joints, nerves, muscles and other structures of the neck. This guide explains the anatomy of the cervical spine and how it works with examples and diagrams.

Cervical spine: Anatomy, ligaments, nerves and injury Biology Diagrams
Learn about the bony, ligamentous, muscular and neural structures of the cervical spine, and how they are affected by various injuries. The article covers the typical and atypical vertebrae, intervertebral discs, cervical plexus, brachial plexus, and more. Learn about the features, joints, ligaments and clinical relevance of the cervical spine, the most superior portion of the vertebral column. The cervical spine consists of seven vertebrae, with the atlas and axis having unique structures and functions. Learn about the cervical spine, the first seven vertebrae of your spine that support your head, protect your spinal cord and allow neck movements. Find out about the muscles, ligaments, disks, nerves and arteries that are involved in your cervical spine and the common conditions that affect it.

Learn about the cervical spine, the upper part of your spinal column that supports your head and allows for neck movement. Find out how cervical spine disorders can cause pain, numbness, or weakness and what surgical or non-surgical treatments are available.

