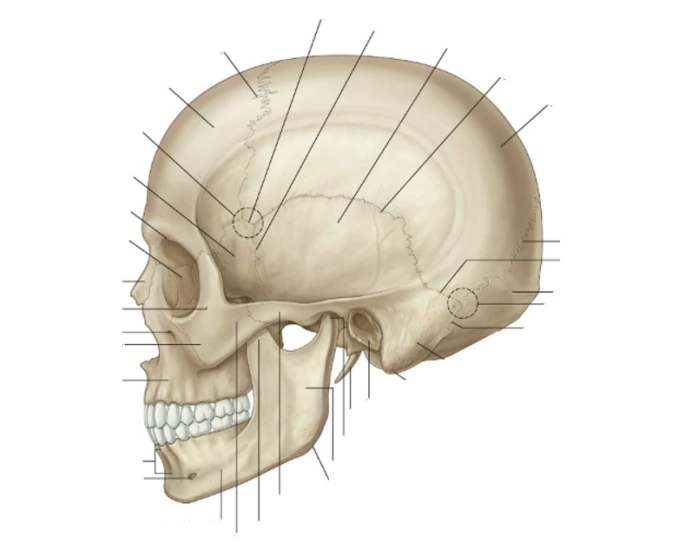
Diagram of Sutures of the skull Biology Diagrams (a) Sutures join most bones of the skull. (b) An interosseous membrane forms a syndesmosis between the radius and ulna bones of the forearm. (c) A gomphosis is a specialized fibrous joint that anchors a tooth to its socket in the jaw. Suture. All the bones of the skull, except for the mandible, are joined to each other by fibrous joints called The sutures of the skull, also referred to as the cranial sutures, are fibrous joints that connect the bones of the skull.They appear as intricate thin lines that mark the adherence between the bones and the growth and closure of the cranial fontanelles. The dense fibrous tissue that connects the sutures is made mostly out of collagen. These joints are fixed, immovable, and they have no cavity. Sutures are fibrous joints where the skull bones meet. They are immovable and tightly locked together. This makes sure the skull stays strong and protects the brain. Human skull sutures have changed a lot over time. One big change was the sutures staying open longer to let the brain grow. This helped our brains get bigger.Sutures in Skull

Introduction to Skull Sutures. The human skull is made up of many bones held together by cranial sutures. These sutures protect the brain and let it grow and expand. They are key to understanding the skull and how humans evolved. Definition and Purpose. Cranial sutures are special joints that link the skull bones. They keep the skull together

Acibadem Health Point Biology Diagrams
The cranial cartilaginous joints (or synchondroses) are located at the base of skull. They are formed by fibrous cartilage tissue. They are formed by fibrous cartilage tissue. In most synchondroses, the cartilage layer between the bones persists only until a certain age, after which the cartilage is replaced by bone tissue and synchondrosis The human skull is a complex and intricate structure, consisting of 22 bones that are fused together by a network of fibrous joints called sutures. Sutures of the skull play a crucial role in the development and growth of the human head, allowing for the expansion and contraction of the brain during different stages of life. In this article, we
Skull sutures are fibrous joints with the periosteum externally and the outer layer of dura mater continuous over and under them. Their wavy appearance affords increased contact surface area between adjacent bones, supporting the strength of the joint. Named sutures divided by their general location include: calvarial. coronal suture. sagittal There are 17 named sutures on the human skull. Key Terms. suture: A fairly rigid joint between two or more hard elements, such as the bony plates of the skull. A suture is a type of fibrous joint (or synarthrosis) that only occurs in the skull. The bones are bound together by Sharpey's fibers, a matrix of connective tissue which provide a

Joints of the skull. Skull sutures Biology Diagrams
This guide will make you an expert on skull suture joints in the skull. You'll be ready for advanced studies in medicine or anatomy. Understanding Skull Sutures. The human skull has many cranial suture types. Each one plays a key role in keeping the skull strong. The coronal, sagittal, and lambdoid sutures are very important. The structure of the skull is a highly detailed and complex design. In all, there are 22 bones comprising the entire skull, excluding the 3 pairs of ossicles located in the inner ear. The bones of the skull are highly irregular. Most of the bones of the skull are held together by firm, immovable fibrous joints called sutures or synarthroses. These joints allow the developing skull to grow both