directional Signaling between Stem Cells and Biology Diagrams 1.2 Genetic Engineering 1.2.1 Genetic Circuits. Design and construction of genetic circuits (the synthetic biology variant of metabolic engineering) has been applied to a wide range of cellular regulation processes. It is known that many cellular regulatory mechanisms are encoded on the DNA levels as regulatory motifs, such as promoters, repressors, oscillators, etc. [5].

Cell cycle progression is controlled by regulatory proteins that act as molecular switches, responding to internal and external signals to either promote or halt division. Among the most significant regulators are cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and cell cycle inhibitors. Cyclins. Cyclins regulate cell cycle timing by activating CDKs. Representation of the cell cycle as being composed of three linear and repetitive series of S phase (S), mitosis (M) and cytokinesis (C). (A) In this simplified model, the three series of events would be regulated individually and coupled to cell growth in an unknown manner.(B) In reality, they are coupled to one another more directly through checkpoint mechanisms. An emerging and critical feature of designing circuits for these applications is their genetic stability. 41 Introducing gene circuits into host cells can impose a fitness cost by creating a metabolic or resource burden or from expression of a toxic protein product. 42, 43, 44 Cells harboring mutations that abrogate circuit function can

Cooperative assembly confers regulatory specificity and ... Biology Diagrams
A newly identified cell-cycle master regulator protein, GcrA, together with the CtrA master regulator, are key components of a genetic circuit that drives cell-cycle progression and asymmetric polar morphogenesis in Caulobacter crescentus.The circuit drives out-of-phase temporal and spatial oscillation of GcrA and CtrA concentrations, producing time- and space-dependent transcriptional
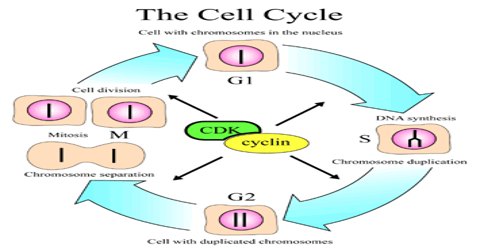
Disruptions in these regulatory mechanisms can lead to diseases such as cancer and genetic disorders, highlighting their biological significance. where genes involved in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis may be improperly silenced or activated. Histone methylation also affects chromatin structure but in a more context-dependent manner THE cell cycle is the sum of the processes by which cells replicate. That process, involving the replication and redistribution of all cellular components, requires the synthesis of many proteins, including constituents of cellular structures and organelles, enzymes that catalyze the many anabolic and catabolic processes required for their replication and distribution, as well as the

Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes: Mechanisms and Complexities Biology Diagrams
The reciprocal regulation of CtrA and GcrA at a transcriptional level has been suggested to form an oscillating genetic circuit that drives the cell cycle 8,12. Notably, a synthetic gene circuit consisting of a tunable band-pass filter (Fig. 4Db) regulating NGN3 expression synchronized to cell stage-specific PDX1 expression and β-cell-specific MAFA The second approach to understanding cell cycle regulation was the genetic analysis of yeasts, pioneered by Lee Hartwell and his colleagues in the early 1970s.Studying the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, these investigators identified temperature-sensitive mutants that were defective in cell cycle progression.The key characteristic of these mutants (called cdc for cell division cycle

