Ecology Day 2 notes Photo by Biology Diagrams A food chain is a fundamental concept in ecology, illustrating how energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem. Food chains reveal the relationships between organisms, showing how each organism plays a role in maintaining ecological balance. Food chains and food webs model feeding relationships in ecosystems. They show how energy and materials are transferred between trophic levels when consumers eat producers or other organisms. A food web is a diagram of feeding relationships that includes multiple intersecting food chains.

Understanding food chains is vital, as they explain the intimate relationships in an ecosystem. A food chain shows us how every living organism is dependent on other organisms for survival. The food chain explains the path of energy flow inside an ecosystem. In other words, the linear model of ecosystems, the food chain, is a hypothetical, overly simplistic representation of ecosystem structure. A holistic model—which includes all the interactions between different species and their complex interconnected relationships with each other and with the environment—is a more accurate and descriptive Food webs are not linear because they show relationships among multiple trophic levels for organisms all at once. They summarize all of the food chains and relationships in an ecosystem or community. A food web reveals the different ways that plants and animals stay connected.

Food Chain: Definition, Types, Examples, FAQs Biology Diagrams
Food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. A food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem. Food Chain and Food Web both show the direction of the flow of energy and nutrients in the ecosystem. The food chain is a linear representation of organisms along the The food web represents multiple interconnected food chains and the complex relationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers. Organisms are arranged into different
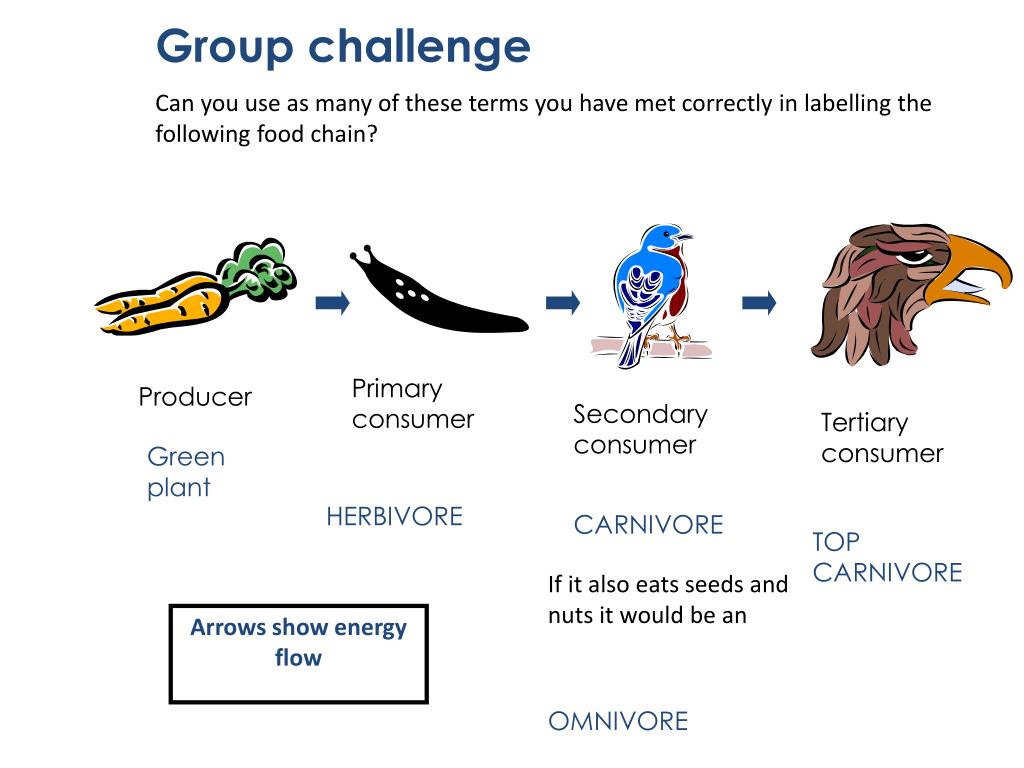
Images of the food chain are intricate representations of the energy flow within ecosystems. They depict the interconnectedness of organisms, where producers like plants utilize sunlight to create their own food. This energy is then transferred to primary consumers, typically herbivorous animals, who feed on the producers. In turn, secondary consumers, such as carnivorous animals, consume the

