Fat Anatomy Diagram Stock Illustration Biology Diagrams Body fat is so much more than storage. Adipose tissue interacts with your entire body to maintain your metabolic homeostasis. Through chemical signals and adaptive responses, adipose tissue could even be said to function with intelligence — at least in the sense that other body systems do. Body composition. The composition of a human body may be considered from different perspectives. The human anatomy model (Fig. 30) divides the body into the following systems: muscular; skeletal; adipose tissue (body fat) the others (inner organs, etc.) Figure 30 Body composition - anatomy model. The chemical (Fig. 31) model consists of Anatomy of fat. Under a microscope, fat cells look like bulbous little spheres. The median turnover for fat cells is about 8.4 percent a year, with half of the fat cells in the body replaced
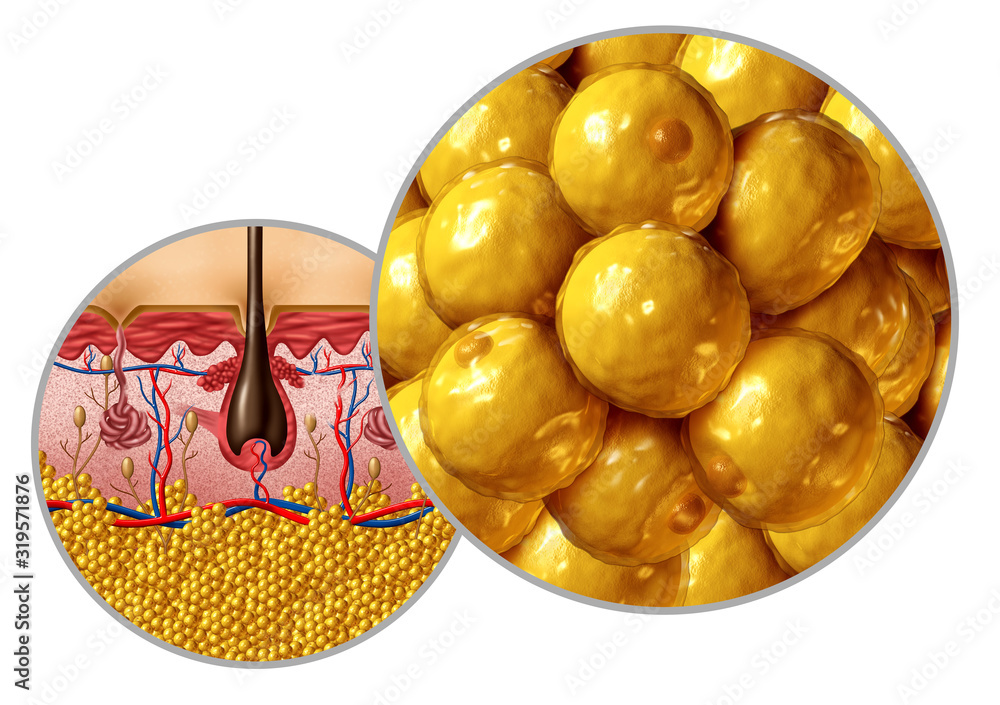
Like the obesity epidemic, our understanding of adipocytes and adipose tissue is expanding. Just in the past decade, substantial advances have led to new insights into the contributions of adipose tissue to normal physiology and obesity-related complications, which places adipocyte biology at the epicenter of a global pandemic of metabolic diseases. In addition to detailing the types Adipose tissue, often referred to as body fat, is a fascinating and vital component of the human body. The anatomy and structure of adipose tissue are intriguingly complex yet elegantly designed. It is primarily composed of adipocytes, or fat cells, which store energy in the form of lipids. Adipose tissue can be found in a number of different places throughout the body. White adipose tissue is the most abundant type of fat in humans. It's distributed within subcutaneous fat, visceral fat, and bone marrow fat.. Subcutaneous fat is found throughout the whole body, in the spaces between the skin and underlying muscles. Visceral fat is predominantly found around the organs in the
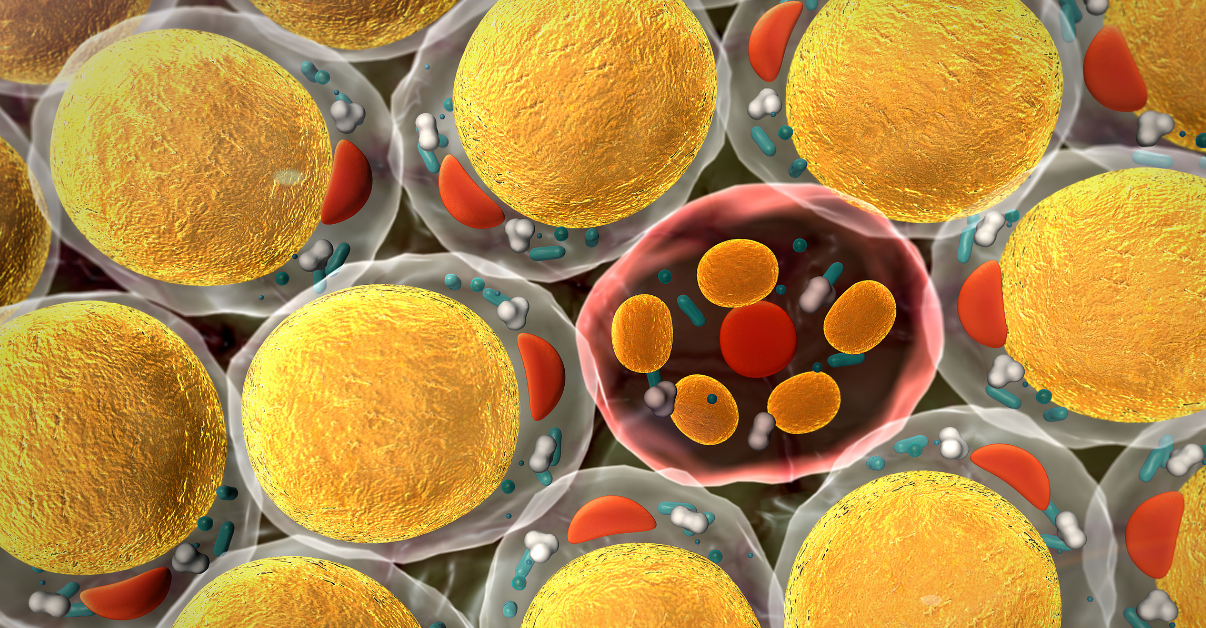
Adipose tissue: Definition, location, function Biology Diagrams
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. [1] [2] It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages.Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions Adipose tissue is distributed within two compartments of the human body: Parietal or subcutaneous fat, which is embedded in the connective tissue under the skin ; Visceral fat, which surrounds the internal organs, such as eyeballs (periorbital fat) or kidneys (perirenal fat capsule).; Like every other tissue, adipose tissue consists of cells and extracellular matrix. The Basics of Body Composition. Body composition is the ratio of fat mass to fat-free mass (ACSM, 2013). Body composition is often expressed as the percentage of total body fat one has, while the remainder is everything else (bone, muscle tissue, organs, teeth, connective tissue, body water etc.) (Kenny et al., 2015).

