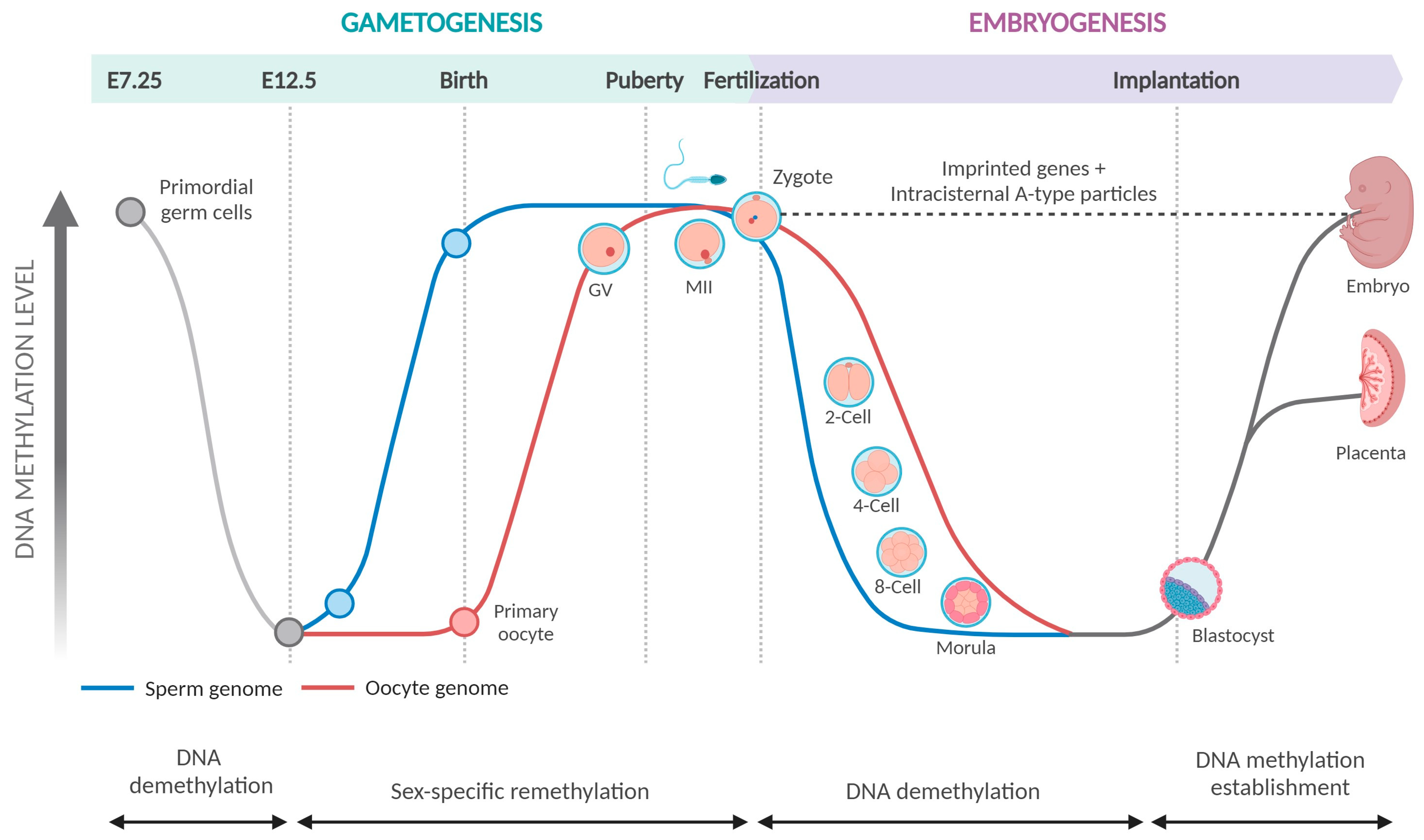
Getting rid of DNA methylation Trends in Cell Biology Biology Diagrams DNA methylation differences between normal brain and glioma may be aberrant events in the tumor, or may reflect differences between the normal brain tissue sample and the methylation patterns of the tumor's cell of origin (Sproul et al., 2012; Witte et al., 2014). In contrast, the differences we report between initial and recurrent tumors are The extent to which DNA methylation changes throughout the cell cycle is currently unknown. Previous studies of methylation during the cell cycle have focused on the maintenance of methylation

Moreover, DNA methylation changes could take place in a single cell type, and the analysis of mixed populations could dilute the effects occurring in a specific cell type. For instance, neutrophils from FMF patients showed a lower level of MEFV gene expression compared with healthy donors, although there were no methylation differences [ 144 ]. DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification with important functions in development. Large-scale loss of DNA methylation is a hallmark of cancer. all of which change the proportion of actively proliferating cells within the population measured. We asked if replication or cell-cycle arrest affects the global levels of methylation or leads Although patterns of DNA methylation appear to be relatively stable in somatic cells, patterns of histone methylation can change rapidly during the course of the cell cycle. Despite this

DNA methylation affects the cell cycle transcription of the CtrA global ... Biology Diagrams
The RNA-Seq data showed that several DEG enriched GO terms and pathways related to the cell cycle. We also observed methylation changes on DNA motifs responsible for the binding of TFs with a role in cell cycle regulation. Thus, we investigated the SFN influence on the HepG2 cell cycle using flow cytometry. DNA methylation undergoes dramatic age-related changes, first described more than four decades ago. Loss of DNA methylation within partially methylated domains (PMDs), late-replicating regions of DNA methylation is recognized as a principal contributor to the stability and regulation of gene expression in development and maintenance of cellular identity (Bird, 2002; Cedar and Bergman, 2012; Jaenisch and Bird, 2003; Reik et al., 2001).Changes in DNA methylation are dynamic and it is still largely unknown how they dictate spatial and temporal gene expression programs (Smith and Meissner

Abstract. The Caulobacter chromosome changes progressively from the fully methylated to the hemimethylated state during DNA replication. These changes in DNA methylation could signal differential binding of regulatory proteins to activate or repress transcription. The gene encoding CtrA, a key cell cycle regulatory protein, is transcribed from two promoters. DNA methylation has been viewed as a stable component of the epigenome, established during development and fixed thereafter. Here we have found that the DNA methylation pattern varies during a single cell cycle, with the global levels of DNA methylation decreased in G(1) and increase during S phase. …