Human anatomy liver Biology Diagrams Learn about the liver, the largest gland in the human body, and its anatomical features, such as lobes, surfaces, ligaments, fissures and recesses. Find out how the liver is supplied by blood, lymph and nerves, and what functions it performs. Anatomy of the Liver. The liver is reddish-brown and shaped approximately like a cone or a wedge, with the small end above the spleen and stomach and the large end above the small intestine. The entire organ is located below the lungs in the right upper abdomen. It weighs between 3 and 3.5 pounds. The liver is a critical organ in the human body responsible for an array of functions that help support metabolism, immunity, digestion, detoxification, and vitamin storage, among other functions. It comprises around 2% of an adult's body weight. The liver is unique due to its dual blood supply from the portal vein (approximately 75%) and the hepatic artery (approximately 25%).

Learn about the liver's location, structure, blood supply, and functions. The liver regulates most chemical levels in the blood, produces bile, and metabolizes drugs and nutrients. Learn about the liver, the largest gland in the human body, and its position, structure, and neurovascular supply. Explore the anatomical lobes, ligaments, recesses, and vessels of the liver with diagrams and 3D models. Liver anatomy consists of two main sections, called lobes, but it's much more than that. It is made up of many parts that handle over 300 important jobs for your body. In this article, we will explore the liver anatomy with its position in the body, its structure, and how it is supplied with blood and nerves.
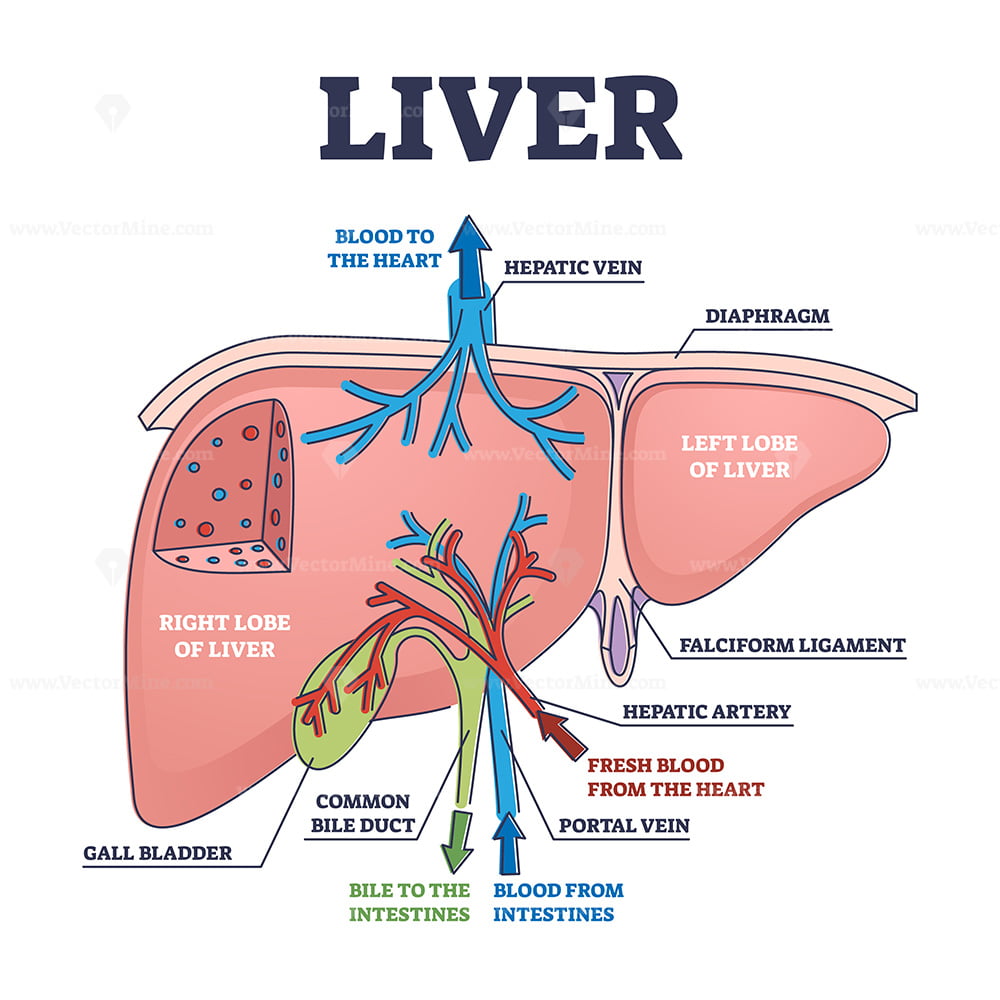
Liver Anatomy Biology Diagrams
Liver Anatomy). The quadrate lobe is located on the inferior surface of the right lobe. The caudate lobe is located between the left and right lobes in an anterior and superior location. The liver is the largest gland in the body and is ideally located to receive absorbed nutrients and detoxify absorbed drugs and other noxious substances. It GENERAL ANATOMY. The liver is the largest organ, accounting for approximately 2% to 3% of average body weight. Ishizaki M, Nemoto M, et al. Close relation between the inferior vena cava ligament and the caudate lobe in the human liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2007;14(3):297-301. doi: 10.1007/s00534-006-1148-7.

Fortunately, the liver has an incredible capacity for regeneration of dead or damaged tissues; it is capable of growing as quickly as a cancerous tumor to restore its normal size and function. Anatomy of the Liver Gross Anatomy. The liver is a roughly triangular organ that extends across the entire abdominal cavity just inferior to the diaphragm.
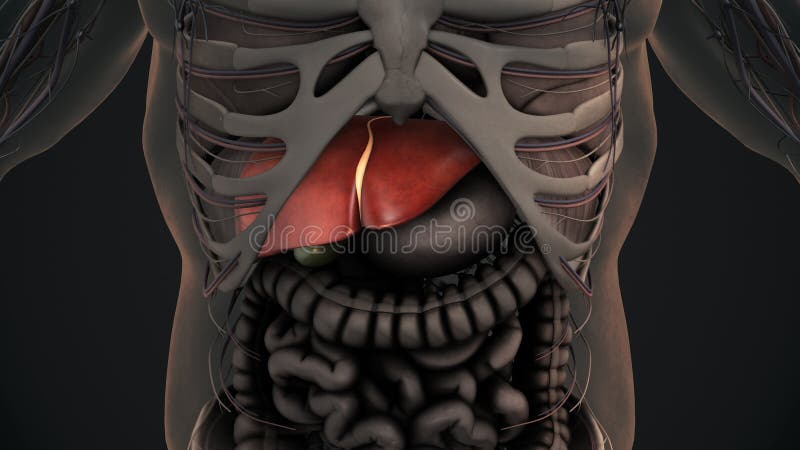
Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Liver Biology Diagrams
The liver, viewed from above, showing the left and right lobes separated by the falciform ligament. The liver is a dark reddish brown, wedge-shaped organ with two lobes of unequal size and shape. A human liver normally weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms (3.3 pounds) [11] and has a width of about 15 centimetres (6 inches). [12] There is considerable size variation between individuals, with the

