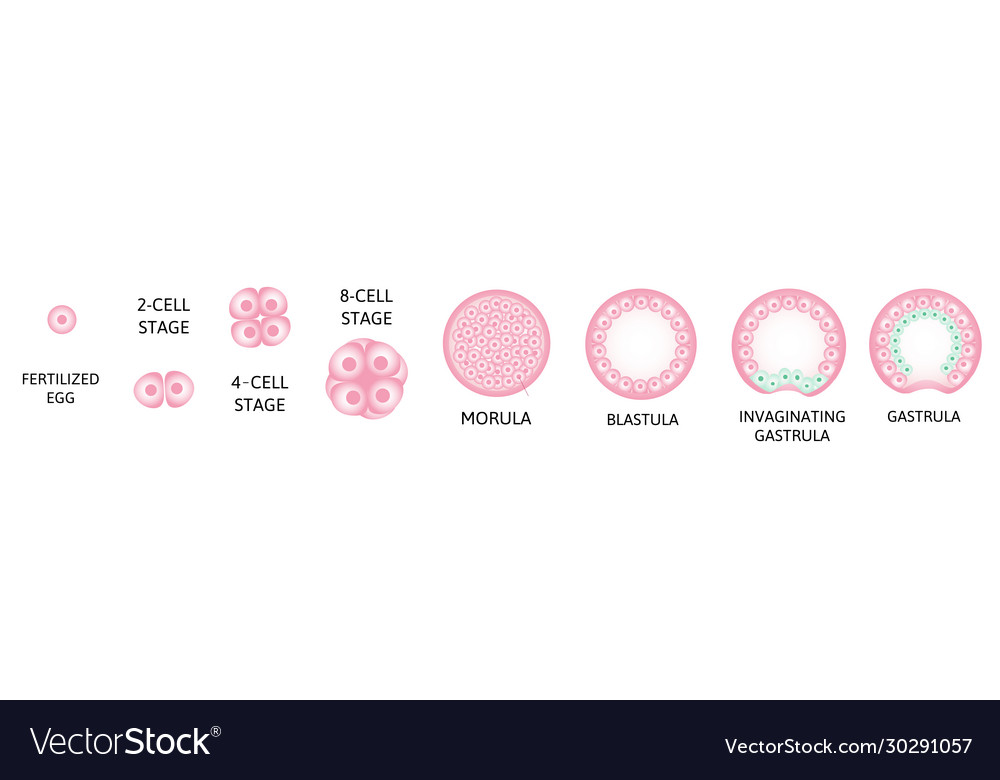
Human embryonic development infographic Royalty Free Vector Biology Diagrams Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\): Embryo at 5 Weeks. An embryo at the end of 5 weeks of development is only 10 mm in length, but its developing eyes, limb buds, and tail are already visible. (Image credit: "Human Embryo 7th Week of Pregnancy" by Ed Uthman is licensed under CC BY 2.0.) During the sixth week, Relating Embryonic Development to the Adult Brain. Embryonic development can help in understanding the structure of the adult brain because it establishes a framework on which more complex structures can be built. First, the neural tube establishes the anterior-posterior dimension of the nervous system, which is called the neuraxis. The Developmental Anatomy. The first eight weeks of human development are called the embryological period. After eight weeks the embryo becomes a fetus, and after birth a neo-nate. There are various ways to determine the age and development of an embryo. It should be noted that age and stage are not the same thing.

In our article on weeks 1-3 of embryonic development you'll learn that the first stage of development starts off with fertilisation. This is the process of male sperm fusing with the female ovum and it's the basis of the embryology covered in the article. TeachMeAnatomy. Part of the TeachMe Series. The medical information on this site A developing human is referred to as an embryo during weeks 3-8, and a fetus from the ninth week of gestation until birth. In this section, we'll cover the pre-embryonic and embryonic stages of development. 24.4: Fetal Development As you will recall, a developing human is called a fetus from the ninth week of gestation until birth.

28.2 Embryonic Development Biology Diagrams
Human embryogenesis is a complicated process by which a fertilized egg develops into an embryo. During the first eight weeks of development, the conceptus shifts from a single-celled zygote into a multi-layered, multi-dimensional fetus with primitively functioning organs. The continued growth and increased intra-embryonic complexity during the first eight weeks of development are highly Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis is the development and formation of the human embryo.It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being.

This page shows some key events of human development during the embryonic period of the first eight weeks (weeks 1 - 8) following fertilization. This period is also considered the organogenic period, when most organs within the embryo have begun to form. Early human development and the chief sources of information on staged human embryos gestation: in human development, the period required for embryonic and fetal development in utero; pregnancy. human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG): hormone that directs the corpus luteum to survive, enlarge, and continue producing progesterone and estrogen to suppress menses and secure an environment suitable for the developing embryo A developing human is referred to as an embryo during weeks 3-8, and a fetus from the ninth week of gestation until birth. In this section, we'll cover the pre-embryonic and embryonic stages of development, which are characterized by cell division, migration, and differentiation.