Human Foetus Anatomy At Week 28 Photograph by Sebastian Kaulitzki Biology Diagrams The fetuses of most mammals are situated similarly to the human fetus within their mothers. [41] However, the anatomy of the area surrounding a fetus is different in litter-bearing animals compared to humans: each fetus of a litter-bearing animal is surrounded by placental tissue and is lodged along one of two long uteri instead of the single
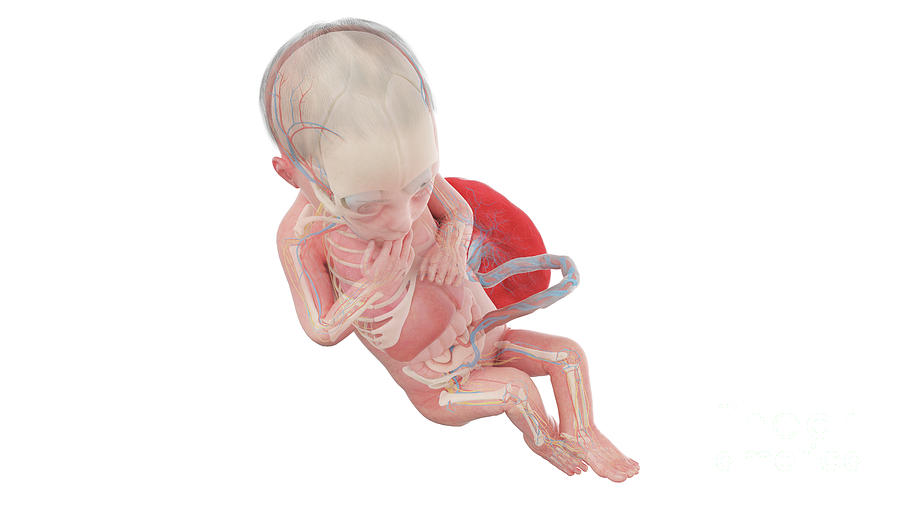
Fetus. An unborn baby from the 8th week after fertilization until birth. Placenta. An organ shaped like a flat cake. It only grows during pregnancy. The fetus takes in oxygen, nutrients, and other substances from the placenta and gets rid of carbon dioxide and other wastes. Umbilical cord. A rope-like cord connecting the fetus to the placenta. The fetal period of human growth and development has become an area of intense study in recent years, due in large part to the development of diagnostic ultrasound. More than 2,000 articles have been published in the last five years describing anatomy and pathology in utero, as reflected in sonographic images. A developing human is referred to as an embryo during weeks 3-8, and a fetus from the ninth week of gestation until birth. In this section, we'll cover the pre-embryonic and embryonic stages of development. 24.4: Fetal Development As you will recall, a developing human is called a fetus from the ninth week of gestation until birth.
28.2 Embryonic Development Biology Diagrams
As you will recall, a developing human is called a fetus from the ninth week of gestation until birth. This 30-week period of development is marked by continued cell growth and differentiation, which fully develop the structures and functions of the immature organ systems formed during the embryonic period.
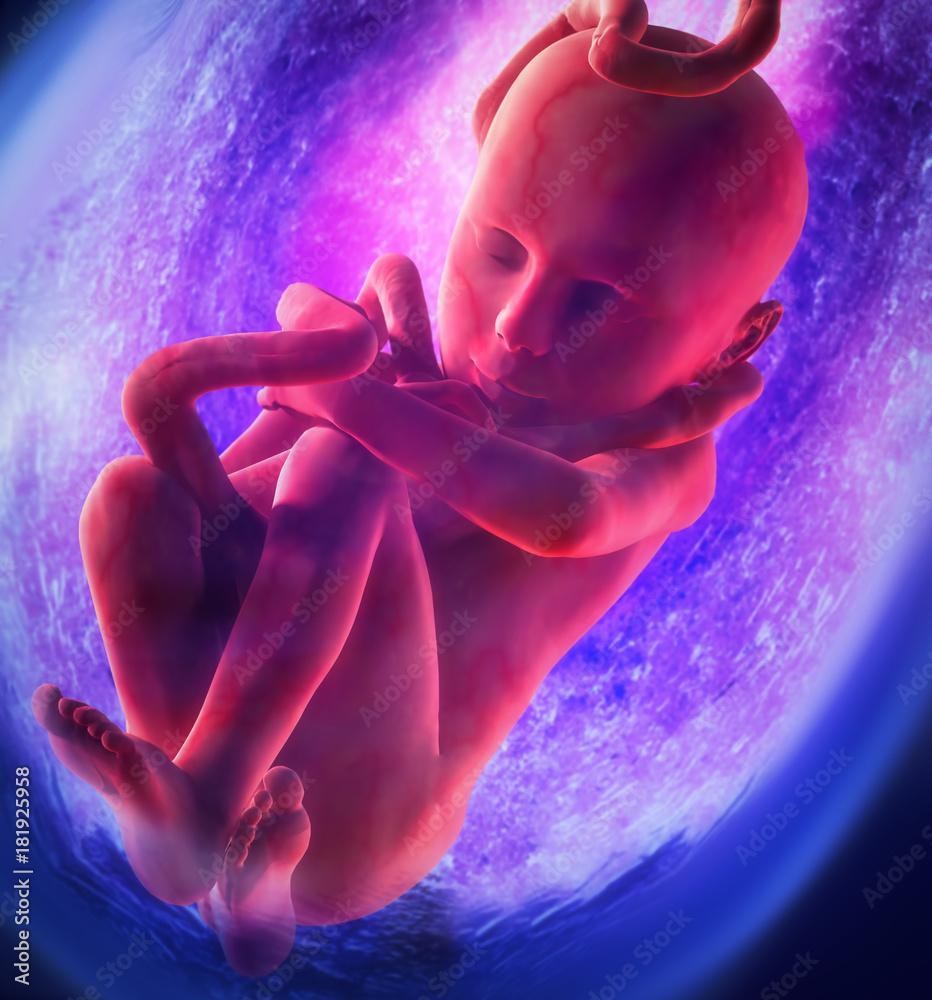

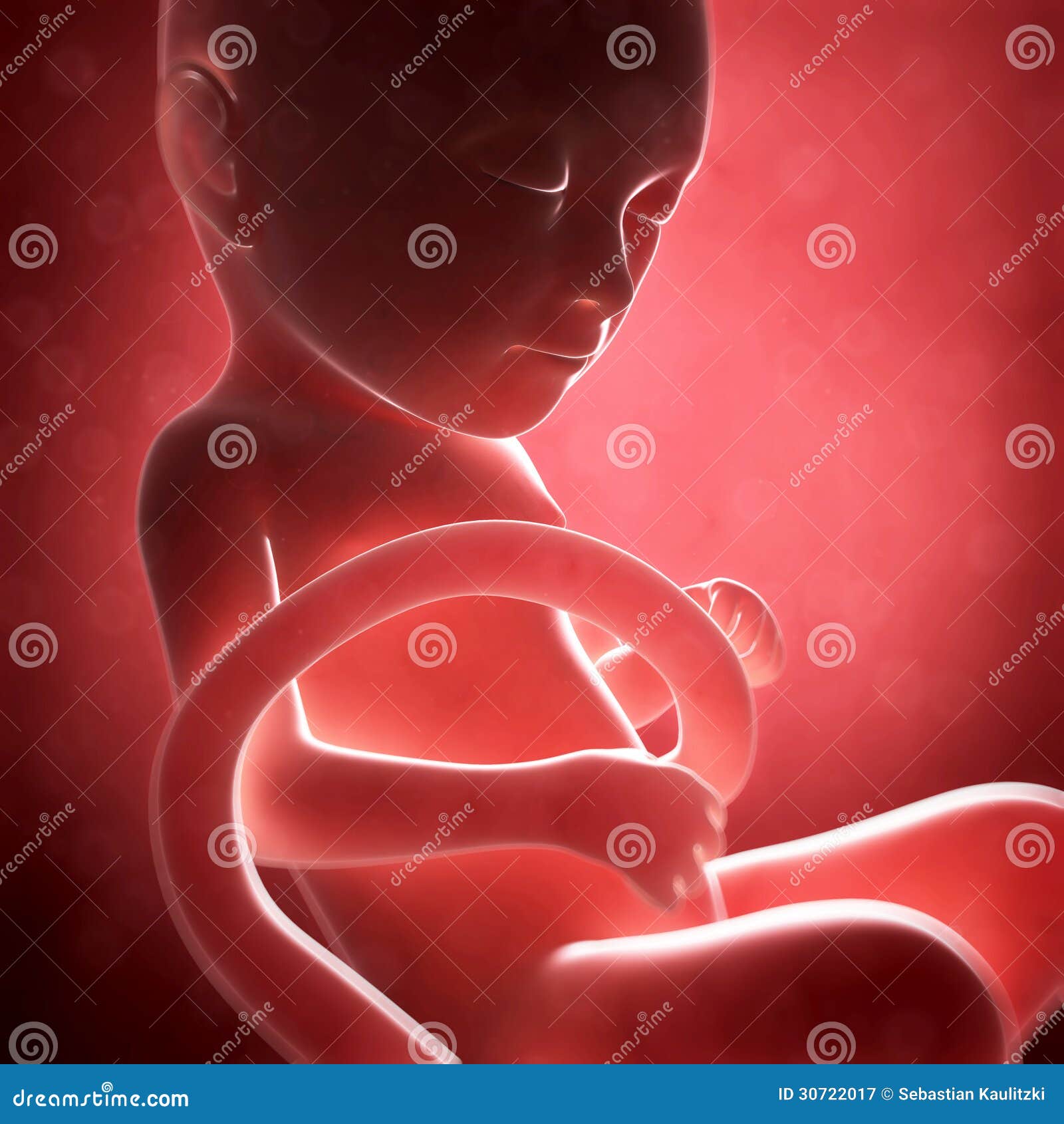
Your baby resembles a tadpole more than a human, but is growing fast. The circulatory system is beginning to form, and cells in the tiny "heart" will start to flicker this week. Your baby's basic anatomy is developing (they even have tiny earlobes now), but there's much more to come. Their embryonic tail has disappeared and they weigh just Anatomy: Fetus in Utero. Amniotic sac. A thin-walled sac that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy. The sac is filled with liquid made by the fetus (amniotic fluid) and the membrane that covers the fetal side of the placenta (amnion). This protects the fetus from injury. It also helps to regulate the temperature of the fetus.
28.3 Fetal Development Biology Diagrams
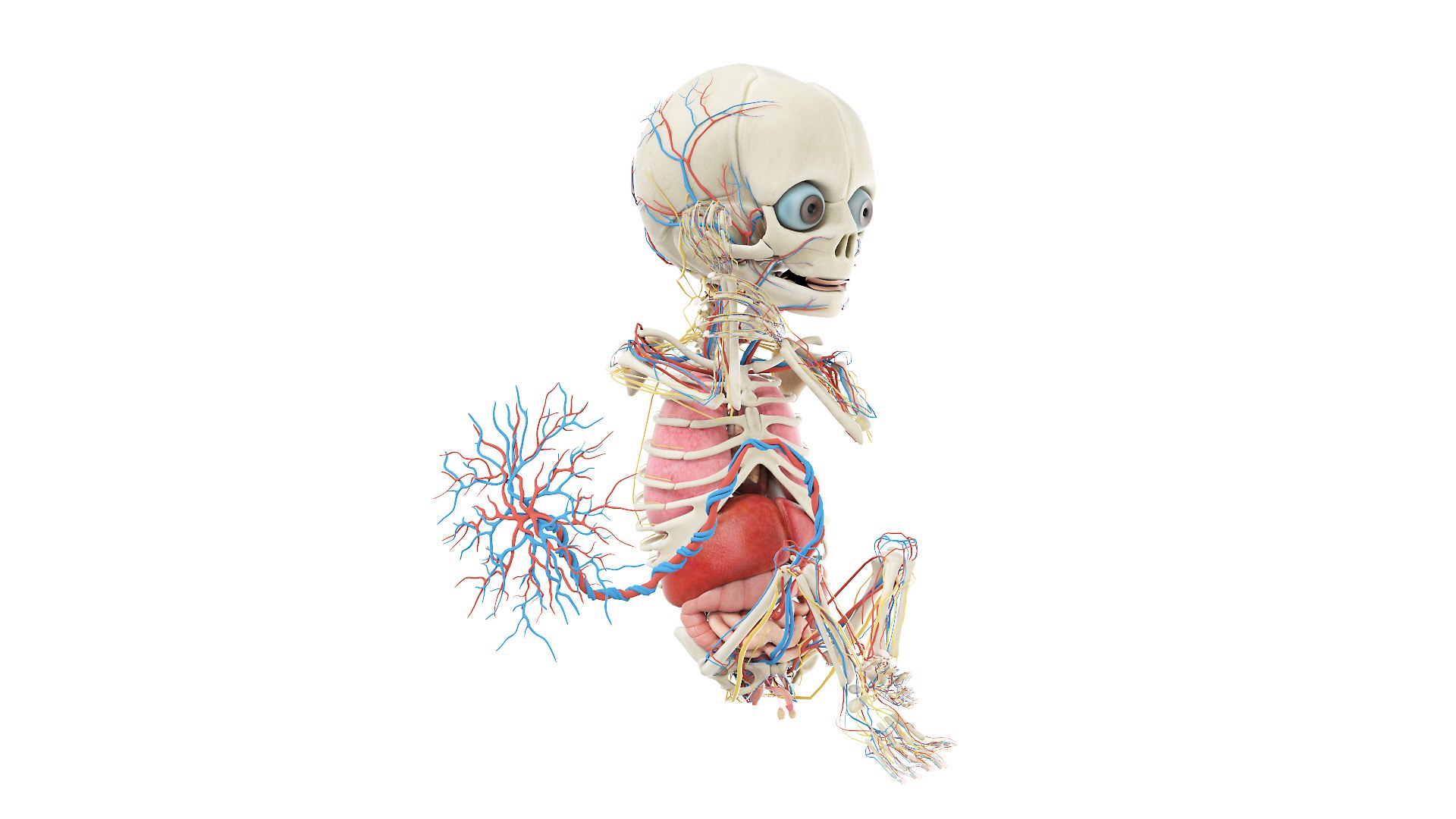
It can be subdivided into distinct gestational periods. The first 2 weeks of prenatal development are referred to as the pre-embryonic stage. A developing human is referred to as an embryo during weeks 3-8, and a fetus from the ninth week of gestation until birth. In this section, we'll cover the pre-embryonic and embryonic stages of Figure 28.3.2 - Fetal Circulatory System: The fetal circulatory system includes three shunts to divert blood from undeveloped and partially functioning organs, as well as blood supply to and from the placenta. Other Organ Systems. During weeks 9-12 of fetal development, the brain continues to expand, the body elongates, and ossification As the embryo enters the fetal stage of development, the placenta becomes functional. The fetus typically measures 30 mm from the crown to the rump and weighs approximately 8 g (shown below). By the end of this stage, the fetus is approximately 15 cm. During this time, several organs can be observed, including the hands, feet, heart, and brain.

