JungleKeyfr Image Biology Diagrams What is Metaphase? Metaphase, a pivotal stage in eukaryotic cell division, is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes along an imaginary central plane termed the metaphase plate. This alignment is a consequence of the intricate interplay between chromosomes and the microtubule network, which ensures precise chromosome segregation. Metaphase Definition. Metaphase is a stage of the cell cycle occurring in both mitosis and meiosis cell division processes. During metaphase in mitosis and meiosis, the chromosomes condense and they become visible and distinguishable during alignment at the center of the dividing cell, to form a metaphase plate at the center of the cell. This alignment occurs along the metaphase plate, an imaginary plane equidistant from the two spindle poles. The positioning of chromosomes is facilitated by interactions between microtubules and kinetochores, protein structures on the chromosome's centromere. These interactions involve a constant push and pull, as microtubules grow and shrink

Metaphase is marked by the alignment of chromosomes at the center of the cell, half way between each of the mitoic spindle poles. Movement is mediated by the kinetochore microtubles, which push and pull on the chromosomes to align them into what is called the metaphase plate. Chromosomes on the metaphase plate are held there tightly by pushing The alignment of the chromosomes, with sister chromatids on each side of the metaphase plate ensures the two new cells will be identical. The sister chromatids represent the two new strands of DNA created from one chromosome during the synthesis stage of interphase. By separating all of these copies into new cells, the two new cells created are identical to the starting cell.
Metaphase - Definition and Stages in Mitosis and Meiosis Biology Diagrams
These chromosomes, carrying genetic information, align in the equator of the cell between the spindle poles at the metaphase plate, before being separated into each of the two daughter nuclei. This alignment marks the beginning of metaphase. [2] Metaphase accounts for approximately 4% of the cell cycle's duration. [citation needed]
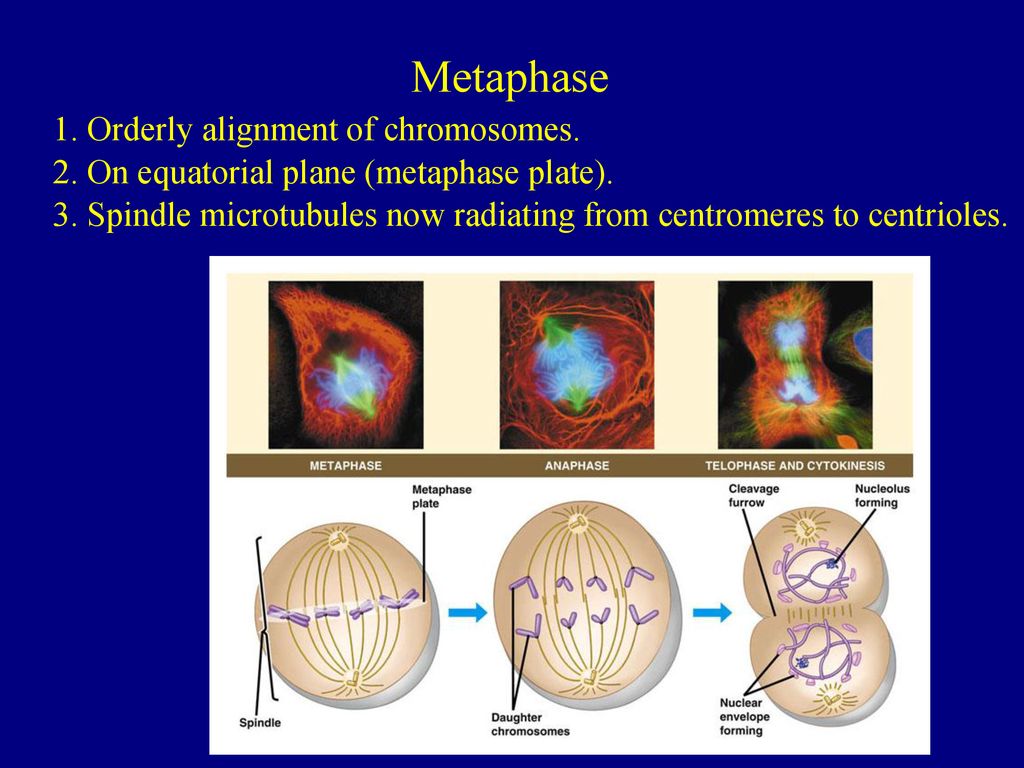
Metaphase, in mitosis and meiosis, the stage of cell division characterized by the alignment of the chromosomes along the midline of the cell. Metaphase is preceded by prophase and is followed by anaphase. The mitotic spindle, which is widest at the middle of the cell and tapers toward its poles,

Metaphase Biology Diagrams
During metaphase, an integral phase of cell division, several crucial events unfold. The mitotic spindle, a complex structure composed of microtubules, forms and attaches to the chromosomes' centromeres. These structures facilitate the precise alignment of chromosomes along the equator of the dividing cell. Additionally, sister chromatids, identical copies of DNA molecules, separate from each Metaphase: Central Alignment. Metaphase is a pivotal stage where chromosomes align in preparation for segregation. This ensures genetic material is evenly distributed between daughter cells. Several events contribute to this precise arrangement, including spindle formation, kinetochore attachment, and equatorial alignment. Understanding metaphase provides insight into cellular function and integrity. Let's explore the specifics of this phase and its significance within mitosis and meiosis. Key Features of Metaphase. Metaphase is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes along the metaphase plate, equidistant from the two spindle poles.
+of+the+cell.jpg)
