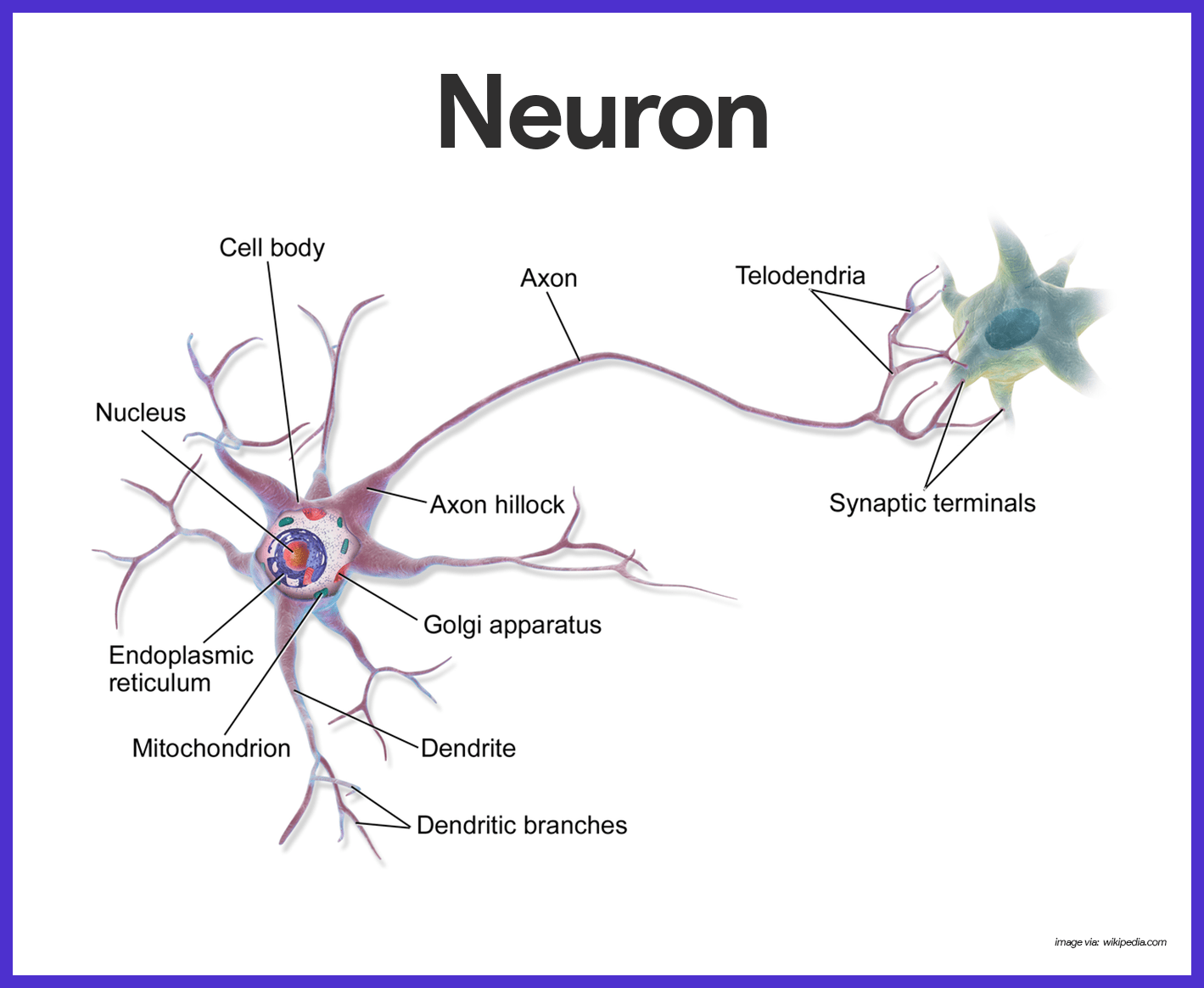
Labeled Neuron Biology Diagrams Neurons are electrically excitable cells that transmit signals throughout the body. Neurons employ both electrical and chemical components in the transmission of information. Neurons are connected to other neurons at synapses and connected to effector organs or cells at neuroeffector junctions. A typical multipolar neuron is comprised of soma or cell body, an axon, and dendrites. The axon is

The Neuron: A Unique Structure Think of a neuron as a tiny messenger in your brain, carrying information and signals all over your body. Imagine it like a mini post office - it has to gather, process, and send messages to different parts. Let's break down its structure into a few key parts: 1. Cell Body (Soma) This is like the command center of the neuron. The cell body contains the Neuronal Structure There are several different types of neurones found in the nervous system. They all contain the same key structural components - the cell body, dendrites, the axon and the axon terminals. Cell Body The cell body holds the nucleus. It is the site of protein synthesis, which occurs on small granules of rough endoplasmic reticulum called nissl substance. In the nervous system
Explain the Structure and Function of Neurons Biology Diagrams
A neuron is a nerve cell that processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system. Neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites (which receive signals), and an axon (which sends signals). Synaptic connections allow communication between neurons, facilitating the relay of information throughout the body. The nervous system consists of two main cell types, neurons and supporting glial cells. The neuron (or nerve cell) is the functional unit of both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The basic functions of neurons can be summarized into four main tasks: receiving signals, integrating these signals/generating signals and transmitting the signals to target Structure of a typical neuron with Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system Neurons are highly specialized for the processing and transmission of cellular signals. Given the diversity of functions performed in different parts of the nervous system, there is a wide variety in their shape, size, and electrochemical properties.

Neurons are the cells of chemical communication in the brain. Human brains com- prise tens of billions of neurons, each linked to thousands of other neurons. Thus, the brain has trillions of specialized connections known as synapses. Neurons have many sizes, lengths, and shapes, which determine their functions. Localization within the brain also determines function. When neurons malfunction What Are Neurons? Neurons are like the communication wires of the body. These specialized cells transmit information throughout our nervous system, allowing us to think, feel, and respond to our environment. Think of your brain as a bustling city, with each neuron acting as a communication line that keeps everything running smoothly.

What is the structure of a typical neuron, and how does it function? Biology Diagrams
NEURON STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION Neurons have four specialized structures that allow for the sending and receiving of information: the cell body (soma), dendrites, axon and axon terminals (see lowest figure). Cell body or soma: The cell body is the portion of the cell that surrounds the nucleus and plays a major role in synthesizing proteins. Dendrites: Dendrites are short, branched Describe the structure of Neuron. The structural and functional unit of the nervous system is the nerve cell or neuron. Approximately 100 billion neuron are present in the nervous system.They are …

