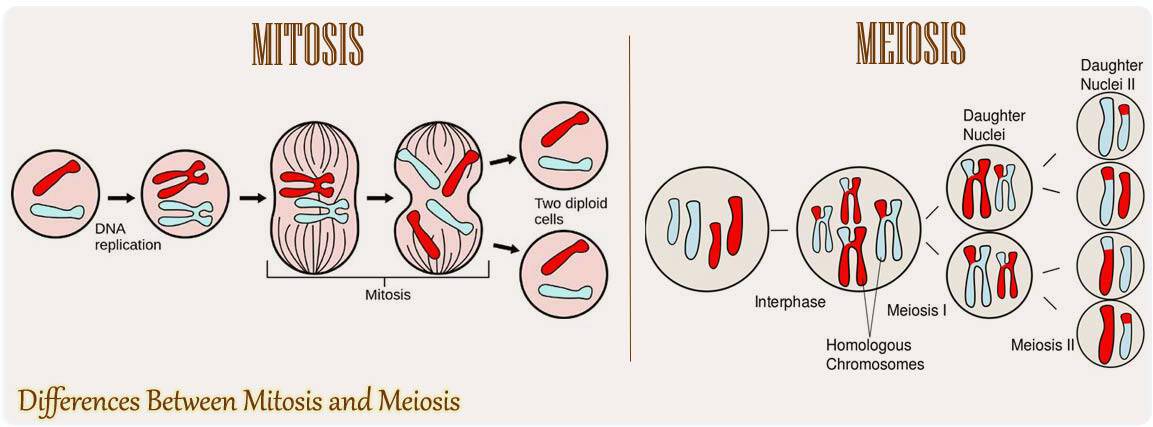
Mitosis vs Meiosis Differences and Similarities the Simplest Explanation Biology Diagrams The difference between mitosis and meiosis I is (A) Sister chromatids separate in mitosis, whereas homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis I (B) The nuclear membrane is absent during mitotic metaphase, but not in meiotic metaphase Learn the differences and similarities between mitosis and meiosis, two types of cell division. Mitosis produces two identical diploid cells, while meiosis produces four non-identical haploid cells for gamete formation. Learn the difference between mitosis and meiosis, two types of cell division processes with different functions and outcomes. Mitosis produces identical diploid cells for growth and repair, while meiosis produces non-identical haploid cells for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity.
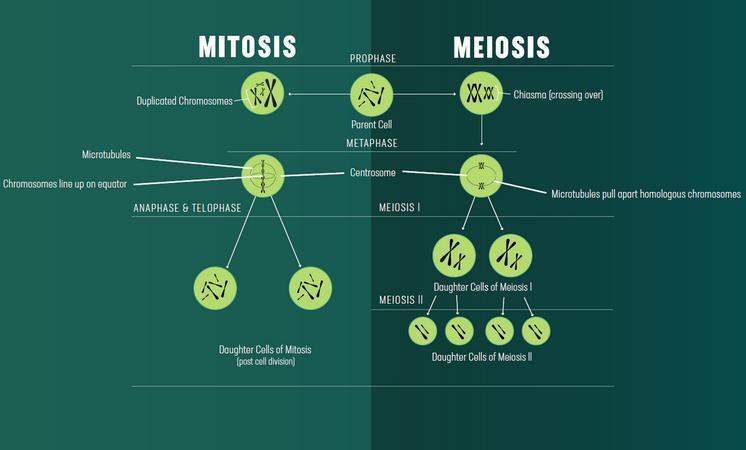
Learn the key concepts of mitosis and meiosis, two types of cell division that occur in living organisms. Compare and contrast their stages, functions, outcomes and examples with a table and diagrams.

Mitosis vs Meiosis: 14 Main Differences Along With Similarities Biology Diagrams
Learn the key differences and similarities between mitosis and meiosis, two types of cell division processes in biology. Mitosis produces identical cells for growth and repair, while meiosis produces genetic variations for sexual reproduction.

Learn the differences between mitosis and meiosis, the two types of cell division in eukaryotes. Mitosis produces identical daughter cells for growth and repair, while meiosis produces non-identical daughter cells for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity. Learn the key differences and similarities between mitosis and meiosis, two cell division processes in eukaryotes. Mitosis produces identical cells for growth and repair, while meiosis produces diverse cells for reproduction.

10 Key Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis Biology Diagrams
Learn the meaning, function and occurrence of mitosis and meiosis, two types of cell division in biology. Compare and contrast their features, such as number of divisions, chromosomes, crossing over and type of reproduction.