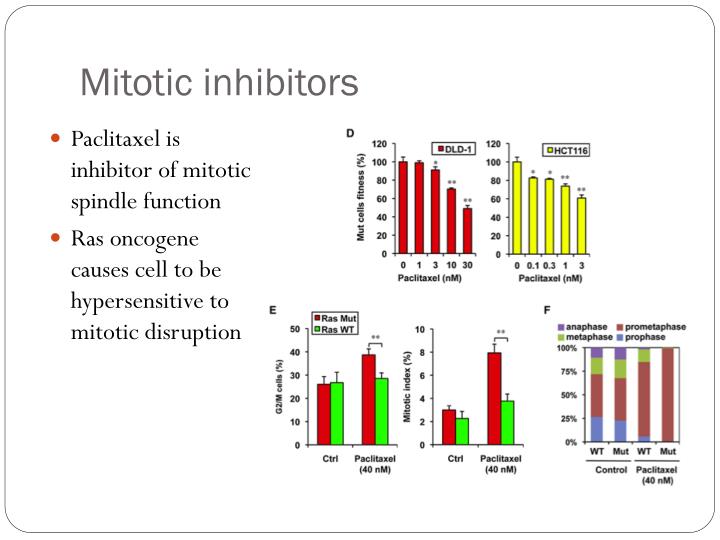
mitotic therapies can we improve on tubulin agents Biology Diagrams Mitotic inhibitors bind to tubulin and inhibit its polymerization into microtubules. Microtubules are structures responsible for pulling the cell apart when it divides. Mitotic inhibitors affect cancer cells more than normal cells because cancer cells divide (mitotic cell division) more rapidly therefore are more susceptible to mitotic inhibition. The development of mitotic kinase inhibitors came as an outgrowth of studies on the molecular mechanisms of the cell cycle in the 1990s [38-40], which promised the development of precise inhibitors of mitosis without the toxic sequelae of classical chemotherapeutics. Yet for all the initial excitement, mitotic kinase inhibitors have now been A mitotic inhibitor, microtubule inhibitor, or tubulin inhibitor, is a drug that inhibits mitosis, Therapy with combination of two or more drugs which have various binding sites and/or different mechanism of action but have non overlapping adverse effects. This would allow use of drugs in low concentration what reduce strength of side
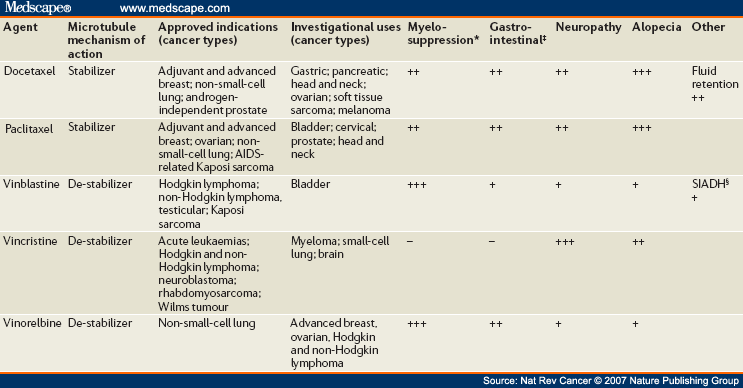
Highly selective inhibitors developed against these targets showed robust cytotoxic activity in preclinical models. Similar to MT poisons, these anti-mitotics cause drug-specific and dose-dependent mitotic phenotypes through disruption of mitotic spindle morphology and MT-chromosome attachment or impairment of SAC (figure, bottom). This review aims to outline mitotic kinase inhibitors' roles as potential therapeutic targets and assess their suitability as a stand-alone clinical therapy or in combination with standard treatments for advanced-stage solid tumors, including triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Breast cancer poses a significant global health risk, with TNBC standing out as the most aggressive subtype The latter is accomplished by means of survivin, which is crucial in spindle assembly formation, and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (P21CIP1) that inhibits cell cycle progression at G 1 . Augmentation of HER2 occurs in 20-25 % of breast cancer types, and HER2-targeted therapy (trastuzumab and lapatinib) has been reported to increase
cancer therapies: where they stand Biology Diagrams
Unfortunately, these so-called second-generation of antimitotics, encompassing mitotic blockers and mitotic drivers, have failed in clinical trials. Our recent understanding regarding the mechanisms of cell death during a mitotic arrest pointed out apoptosis as the main variable, providing an opportunity to control the cell fates and influence Targeting the mitotic checkpoint for cancer therapy with NMS-P715, an inhibitor of MPS1 kinase. Cancer Res 2010; 70 : 10255-10264. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Functional redundancy between mitotic kinesins could be amongst the reasons that challenge the clinical efficacy of Eg5 inhibitors [59]. Interestingly, these Eg5 inhibitors induce cell death in combination with taxol even in taxol-resistant cancer cells, highlighting the therapeutic potential of Eg5 inhibition in combination with other