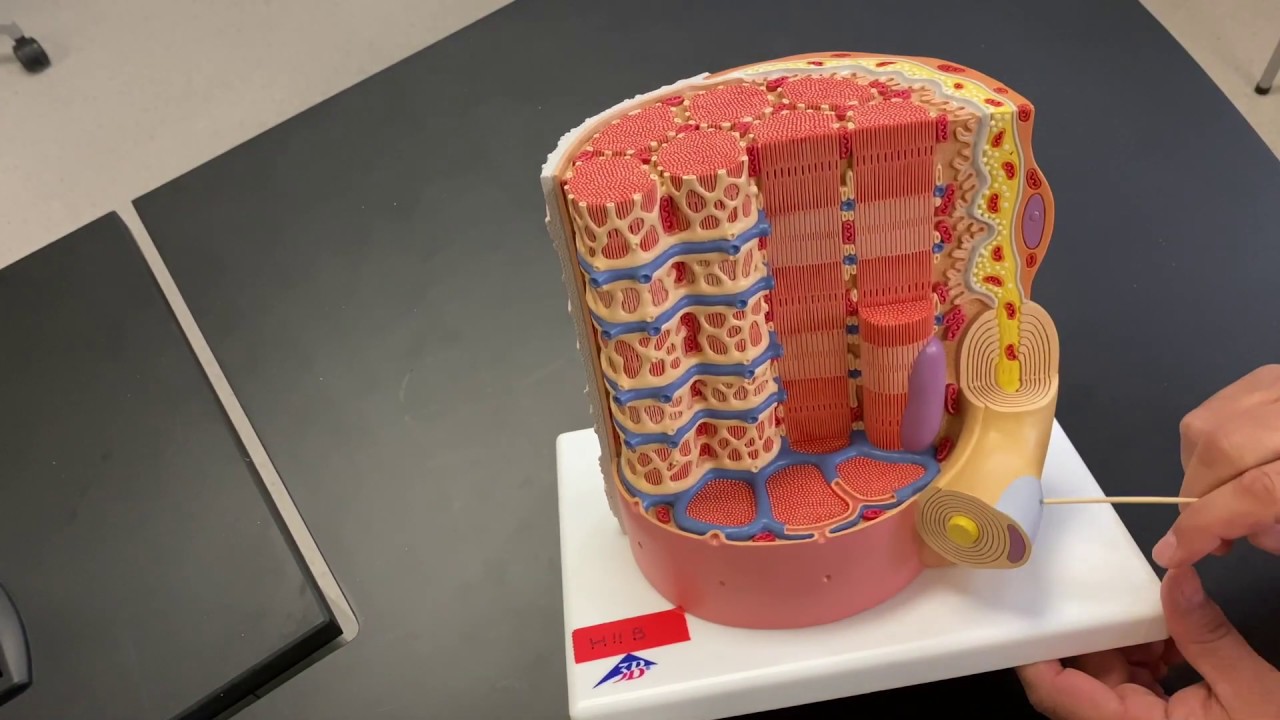
muscle fiber Diagram Biology Diagrams Structure of Skeletal Muscle. A whole skeletal muscle is considered an organ of the muscular system.Each organ or muscle consists of skeletal muscle tissue, connective tissue, nerve tissue, and blood or vascular tissue.. Skeletal muscles vary considerably in size, shape, and arrangement of fibers. They range from extremely tiny strands such as the stapedium muscle of the middle ear to large The smallest contractile unit of skeletal muscle is the muscle fiber or myofiber, which is a long cylindrical cell that contains many nuclei, mitochondria, and sarcomeres (Figure 1) [58]. Each muscle fiber is surrounded by a thin layer of connective tissue called the endomysium. Approximately 20-80 of these muscle fibers are grouped together in a parallel arrangement called a muscle fascicle

The plasma membrane of muscle fibers is called the sarcolemma (from the Greek sarco, which means "flesh") and the cytoplasm is referred to as sarcoplasm (Figure 33.3). Within a muscle fiber, proteins are organized into organelles called myofibrils that run the length of the cell and contain sarcomeres connected in series. Because myofibrils These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue (called "mysia") that enclose it and provide structure to the muscle as a whole, and also compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle (Figure 1). Learn about the different types of muscle fibers in your body, how they work, and what can go wrong. Find out how skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle fibers are structured, function, and vary in speed and endurance.

Anatomy, Skeletal Muscle Biology Diagrams
Learn about the structure and function of muscle fibers, from types and sarcomeres to neuromuscular junctions and connective tissue. Discover how muscle fibers adapt to different activities and diseases, and how they communicate with the nervous system. The musculoskeletal system comprises one of the body's major tissue/organ systems. The three main types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle groups.[1][2][3] Skeletal muscle attaches to the bone by tendons, and together they produce all body movements. The skeletal muscle fibers are crossed with a regular pattern of fine red and white lines, giving the muscle a distinctive
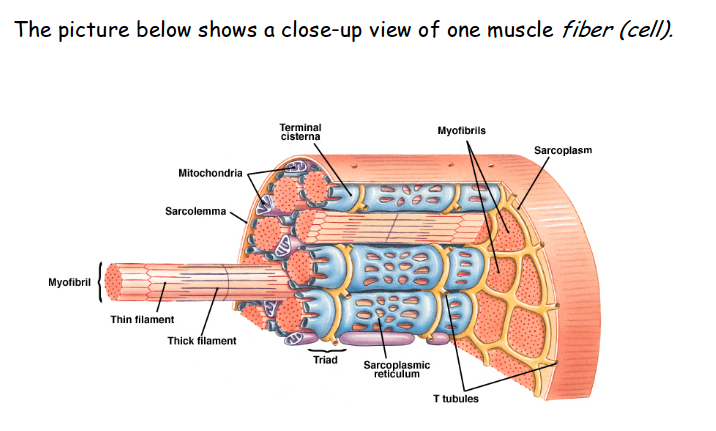
21.1 Anatomy of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems ; 21.2 Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response ; 21.3 The Adaptive Immune Response: The primary metabolic pathway used by a muscle fiber determines whether the fiber is classified as oxidative or glycolytic. If a fiber primarily produces ATP through aerobic pathways it is oxidative. Learn about the structure and function of skeletal muscle fibers, myofibrils, and sarcomeres. Understand the sliding filament process of muscle contraction and the role of calcium ions and proteins.