Plastic In The Food Chain Biology Diagrams How many plastic bags might it have eaten, thinking they were yummy jellyfish? How Does Plastic Get Into the Food Chain? Studies show in 2021, an average of 8 million pieces of plastic will make their way into the ocean. An estimate of 381 million tonnes, and scientists predict it to double by 2034.

On that note, plastic pollution in marine ecosystems can also have an impact on human life. Starting with food safety: Microplastics can enter the human food chain through seafood consumption.The long-term health effects of ingesting microplastics are still being studied, but there are concerns about potential toxicity and other health risks.
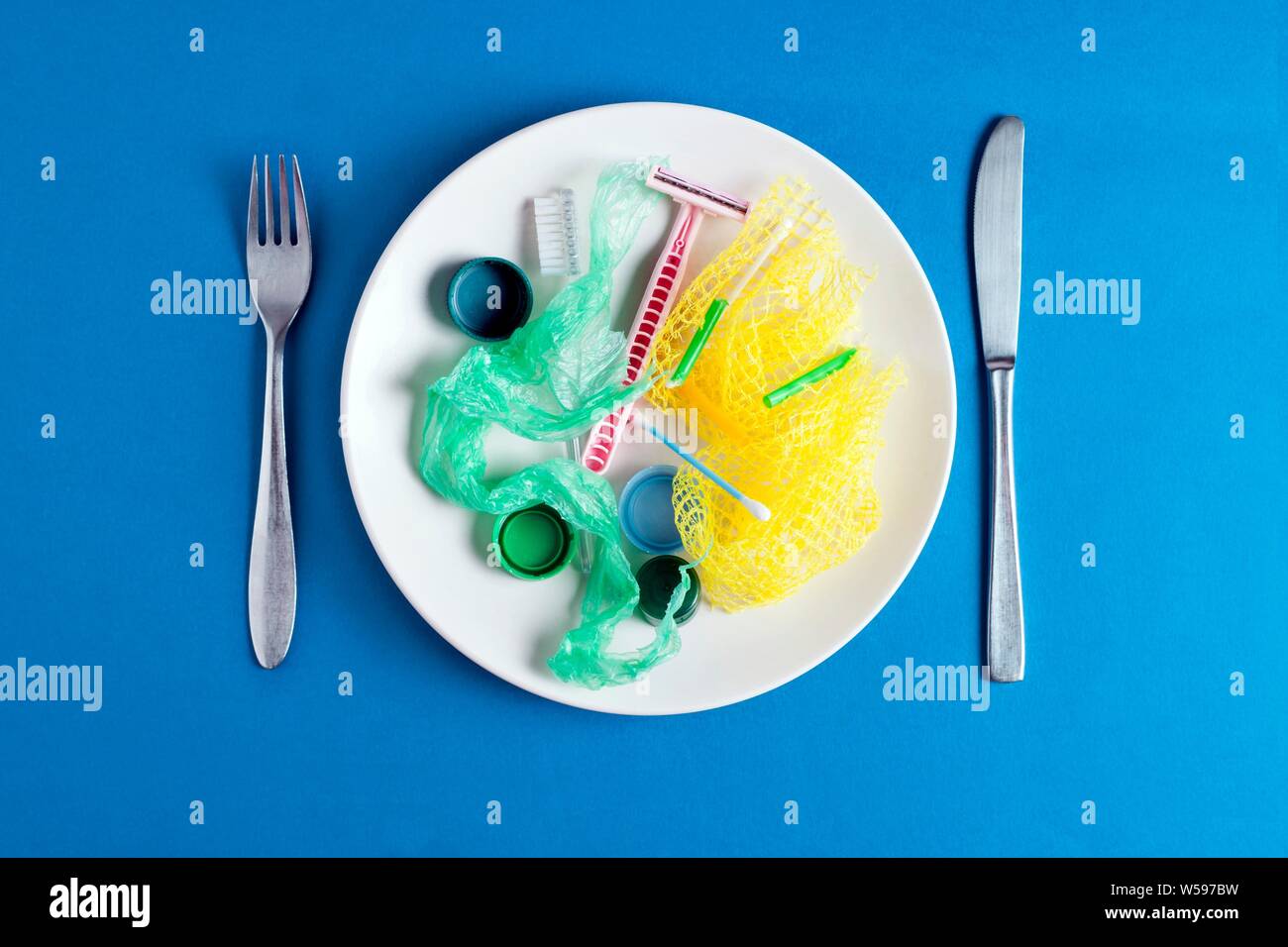

New Link in the Food Chain? Marine Plastic Pollution and Seafood Safety ... Biology Diagrams
In conclusion, humans are frequently exposed to microplastics in food chain, which is considered the most significant among multiple environmental sources. The effect of plastic pollution in the world is a growing concern due to hundreds of thousands of years of durability of plastics in the environment. In recent years plastic pollution in the ocean has become a significant environmental concern for governments, scientists, nongovernmental organizations, and members of the public worldwide. A December 2014 study derived from six years of research by the 5 Gyres Institute estimated that 5.25 trillion plastic particles weighing some 269,000 tons With plastic that moves through the food chain, the attached toxins can also move and accumulate in animal fat and tissue through a process called bio-accumulation. In addition, chemicals are often added to plastic during the production process, to give them some desired properties. These chemicals can in turn leak from the plastic, even when
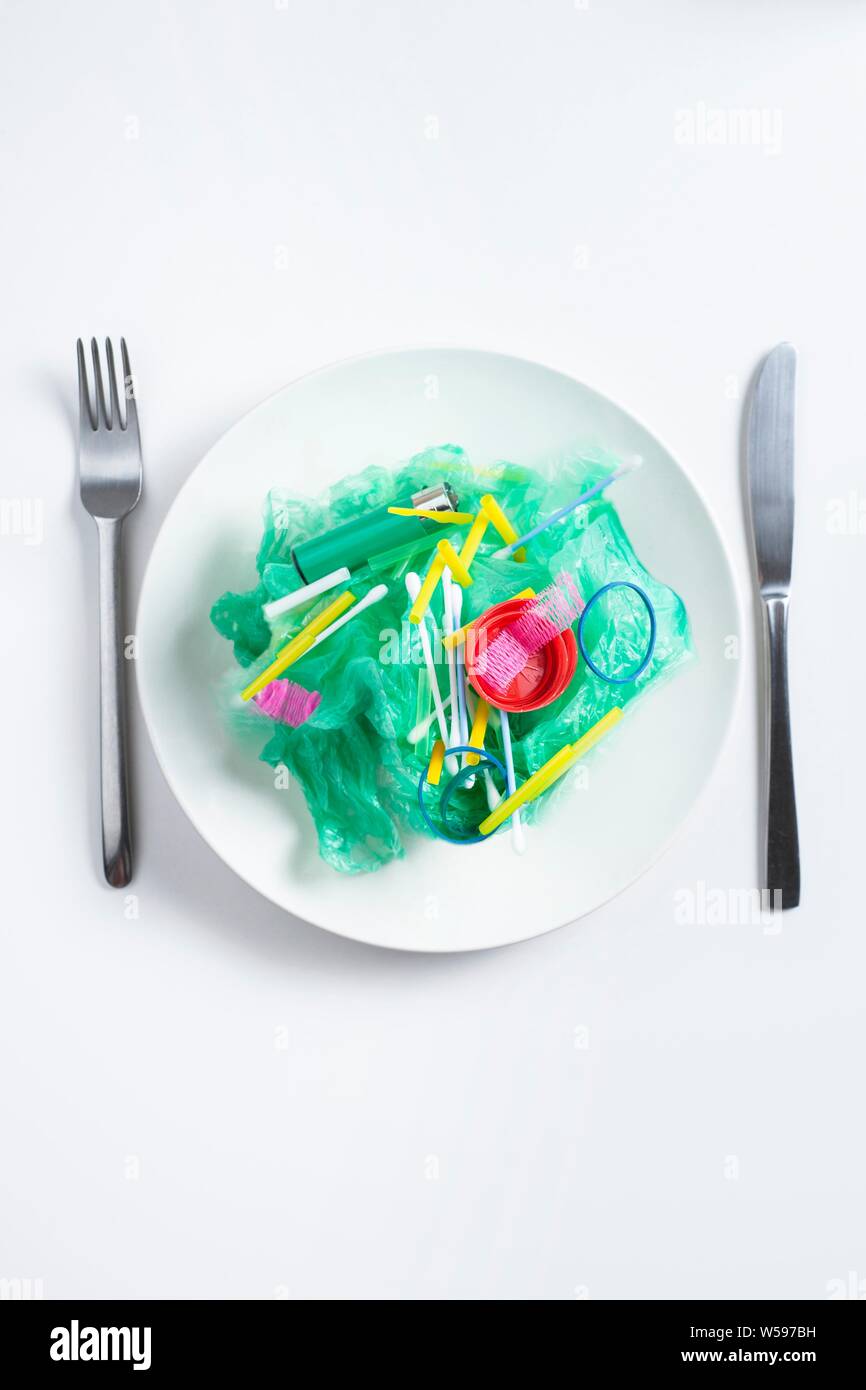

Macro-plastic pollution is found in terrestrial and marine environments and is degraded to micro-particles (MP) and nano-particles (NP) of plastic. These can enter the human food chain either by inhalation or by ingestion, particularly of shellfish and crustaceans. Absorption across the gastrointestinal tract is relatively low, especially for The extent of the impacts of plastic pollution is still largely unknown and remains to be adequately explored. nanoplastics and synthetic polymers in marine food chains, food products and the air we Packaging forms a crucial part of sales, marketing and consumption of goods. In addition, plastic food shopping bags, plastic crockery and Therefore, compared to water bodies, terrestrial ecosystems and soil are more sensitive to plastic pollution (Huang et al., 2022, Kamyab et al., 2023). These microplastics pollute soil and plants in human food chains, affecting physicochemical qualities such as soil pH levels, accumulation, density of bulk, and capacity for holding water,
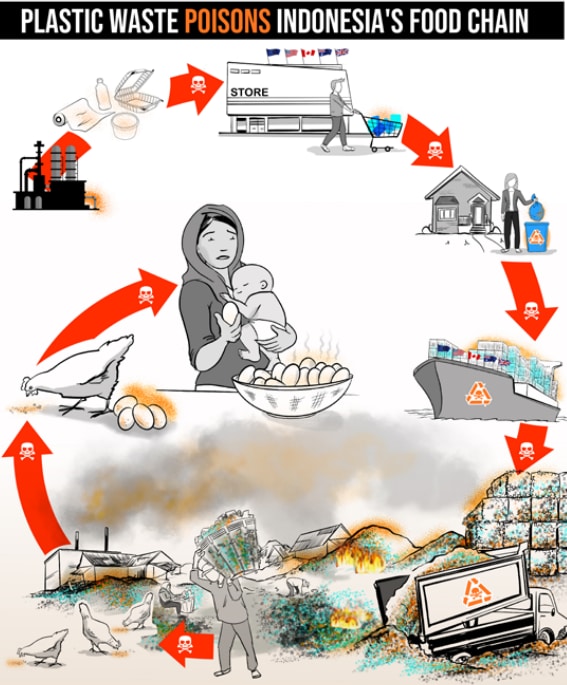
PROTOCOL: Plastics in the food system: Human health, economic and ... Biology Diagrams
Therefore, it is not surprising that with the degree of plastic pollution of marine and freshwater resources, the first information about microbial association with microplastics soon appeared. Escalona Segura G., Gertsen H., Salánki T., van der Ploeg M., et al. Field evidence for transfer of plastic debris along a terrestrial food chain

