Protozoa I protozoan parasites with direct life cycles Flashcards Biology Diagrams The composition of the cell wall differs with each organism. In contrast, protozoa have no cell wall and instead have a pellicle, which is a flexible, proteinaceous covering. Toxoplasma gondii has a complex life cycle involving at least two different hosts. The protozoan reproduces sexually within its primary host, the cat, and releases Excystation, a phase in the life cycle of protozoa, is where dormant cysts transform back into active trophozoites. Mechanisms of Excystation. Once the cyst wall is compromised, the protozoan cell undergoes morphological changes driven by the reactivation of metabolic pathways dormant during the cyst stage. The re-establishment of

This mechanism contributes to the life cycle of Plasmodium, particularly in its transmission via vectors. Locomotory Organelles of Protozoa. Pseudopodia, or "false feet," are extensions of the protozoan cell membrane that allow for crawling and prey engulfment. This method of locomotion enables protozoa to move and interact with their The Protozoa are considered to be a subkingdom of the kingdom Protista, although in the classical system they were placed in the kingdom Animalia. More than 50,000 species have been described, most of which are free-living organisms; protozoa are found in almost every possible habitat. The fossil record in the form of shells in sedimentary rocks shows that protozoa were present in the Pre

Protozoa: Structure, Classification, Growth, and Development Biology Diagrams
Programmed cell death pathways intrinsically affect host-parasite interactions and influence pathogenesis. Activation or inhibition of the host's PCD pathways by parasites may increase survival and persistence in host cells. This review focuses on proteomics studies of PCD mechanisms during host-protozoan parasite interactions. Keywords: Protozoan parasites, motility, cell invasion, protein secretion, cytoskeleton, signaling. Introduction. Protozoan parasites that infect humans are an extremely diverse collection of organisms that spans much of the eukaryotic tree of life . Implicit from this diversity, parasitism as a life style evolved multiple times independently

Programmed cell death (apoptosis) is an important regulator of the host's response during infection with a variety of intracellular protozoan parasites. Parasitic pathogens have evolved diverse strategies to induce or inhibit host-cell apoptosis, thereby modulating the host's immune response, aiding dissemination within the host or facilitating intracellular survival. Cell Size and Structure. The size and shape of Protozoa vary greatly, from 1µm to 50 µm. However, the largest, Balantidium coli, may measure 150 μm. Protozoa are unicellular, having a eukaryotic cell structure with a well-developed nucleus and membrane-bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, Golgi bodies, and lysosomes.. The plasma membrane encloses the cytoplasm that is differentiated
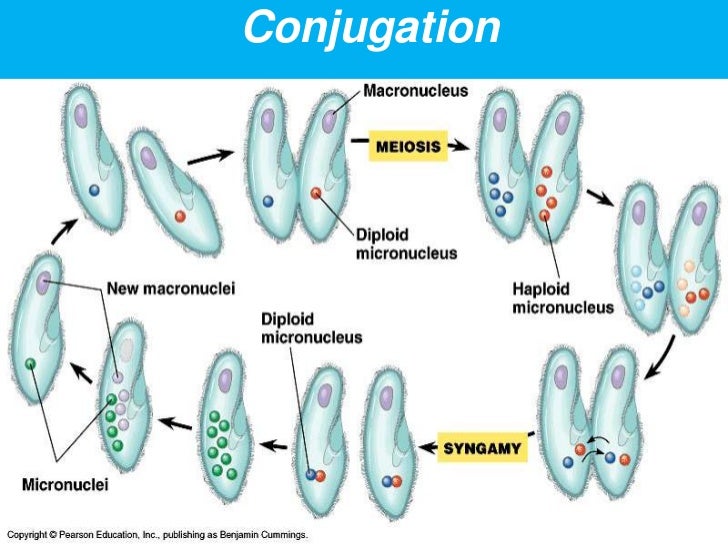
Intracellular protozoan parasites and apoptosis: diverse ... Biology Diagrams
The ability to manipulate host cell processes is another survival tactic. Protozoa can interfere with apoptosis, the programmed cell death mechanism, ensuring the longevity of their host cells and, consequently, their own survival. By modulating apoptotic pathways, they prevent premature cell death, allowing for prolonged infection and replication. c) Cilia and flagella can sweep food along the cell surface toward the cytostome and sometimes line a region of the cell called an oral funnel or oral groove. d) Pseudopodia - Amoeba-like protozoa use their pseudopodia to capture food by extending them out and around the food and fusing them to form food vacuoles. 3.

