Red Wolves Biology Diagrams In the food chain from the grassland ecosystem in Wyoming, two organisms can be identified as both predators and prey. Yellow-pine Chipmunk. Prey: The chipmunk primarily feeds on plants like slender wheatgrass, making it a prey organism. Predator: It also hunts insects and other small animals, which makes it a predator to these organisms. Long-tailed Weasel
Weasels are essential to the animal food chain as prey and predators. They provide a good source of nutrition to organisms that rely on them as food. These small mammals also prey on organisms like voles, ground squirrels, terrestrial insects, mice, frogs, small birds, bird eggs, and rabbits, and thus help regulate their local population within Secondly, we should recognize the importance of conserving these incredible creatures and their habitats. By protecting weasels, we are safeguarding the health and stability of our natural world. To end on a final note, weasels may be small in size, but they are undoubtedly mighty in their impact on the food chain and ecosystem balance.
Weasels Diet By Types Biology Diagrams
Least weasels inhabit meadows, fields, brushy land, or woods. They may take over nests and burrows of mice, moles and voles, lining them with fine grass or fur. This tiny weasel occupies a lower position in the food chain than ermines and long-tailed weasels. It is preyed on by the larger weasels, snakes, owls and cats. Longevity in the Records show everything from ermine to long-tailed weasels being found in predators' stomachs and scat demonstrating they are vulnerable to diverse threats in the wild from top to bottom of the food chain. Avian Predators Owls. As nocturnal hunters, owls pose one of the biggest aerial threats to weasels. Species like the great horned owl and

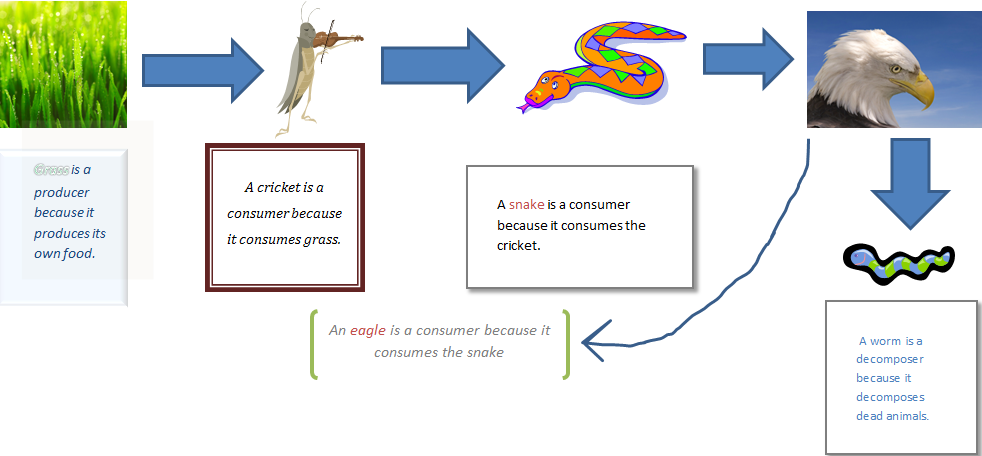
In a grassland food chain, the grass is the producer. It produces food using the sun's energy. The primary consumers follow the producers. Insects like grasshoppers are primary grasslands consumers as they depend on the green plant for their food (herbivores). Occasionally, primary consumers are omnivores as well, such as aardvarks. A food chain helps determine the relationship between different organisms based on their feeding habits. The food chain consists of levels, known as trophic levels, which are defined by the source of energy of the organisms belonging to the particular level. The food chain is a part of the food web and is not as complicated as a food web.

Grassland Food Webs: The Circle of Life in the Plains Biology Diagrams
A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants, grasshoppers, frogs, snakes and hawks (Figure 8.3). In a freshwater aquatic ecosystem like a pond, the organisms in the food chain include algae, small animals, insects and their larvae, small fish, big fish and a fish-eating bird or animal (Figure 8.4). A food chain Mice and other weasel prey aren't attracted to neat, tidy landscapes, so the messier the better. In fact it's a good rule of thumb for creating habitat for most wildlife species, not just weasels and their prey. Not the Top of the Food Chain. Though weasels are highly effective predators, they aren't at the top of the food chain. Consumers in Grassland Food Webs. While grassland producers form the foundation of these ecosystems, the intricate web of consumers plays a vital role in shaping the dynamics and maintaining the balance within grassland biomes.These consumers, ranging from herbivores to predators, are intricately woven into the fabric of the food web, each fulfilling a unique ecological niche and contributing

