Replication and the Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams Life cycle of the cell Onion cells in different phases of the cell cycle.Growth in an 'organism' is carefully controlled by regulating the cell cycle. Cell cycle in Deinococcus radiodurans. The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell
.jpg)
But animals and plants still use the cell cycle to produce new cells within their tissues. This allows these multicellular organisms grow and heal throughout their lifespans. Function of Cell Cycle. Because cells reproduce by dividing, new "daughter" cells are smaller than their parent cells, and may inherit the bare minimum of cellular

Cell Cycle: Definition, Phases, and Diagram Biology Diagrams
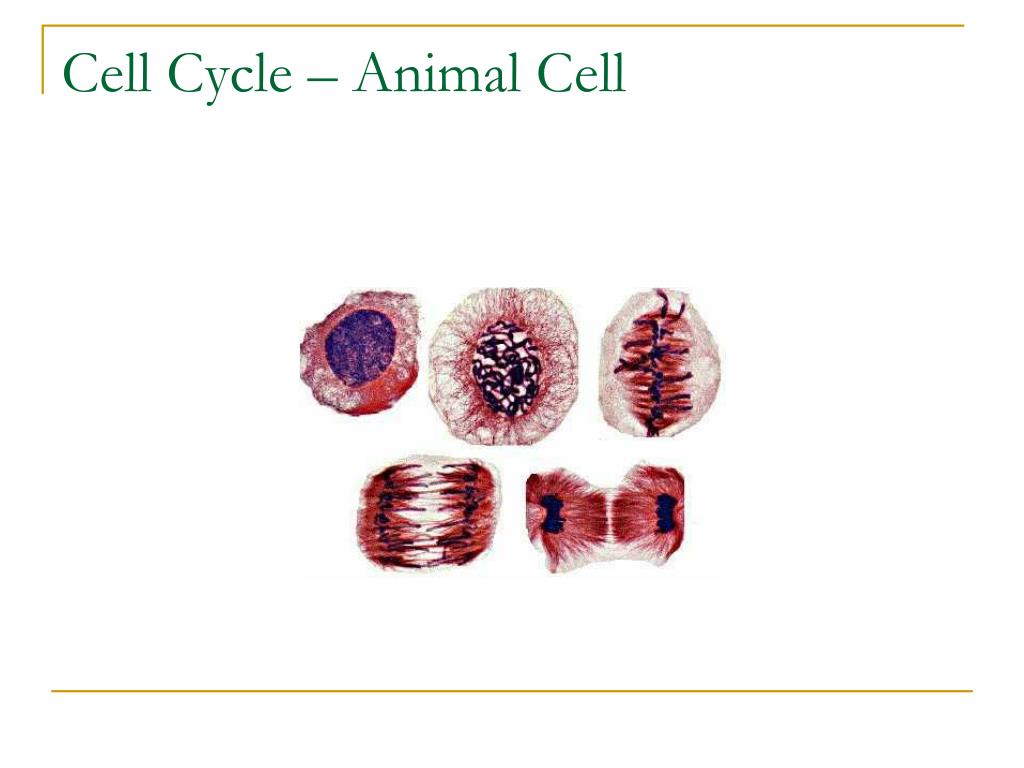
The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA replication, and nuclear and cytoplasmic division that ultimately produces two identical (clone) cells. The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. Animal cell mitosis is divided into five stages—prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase—visualized here by light microscopy with fluorescence. Mitosis is
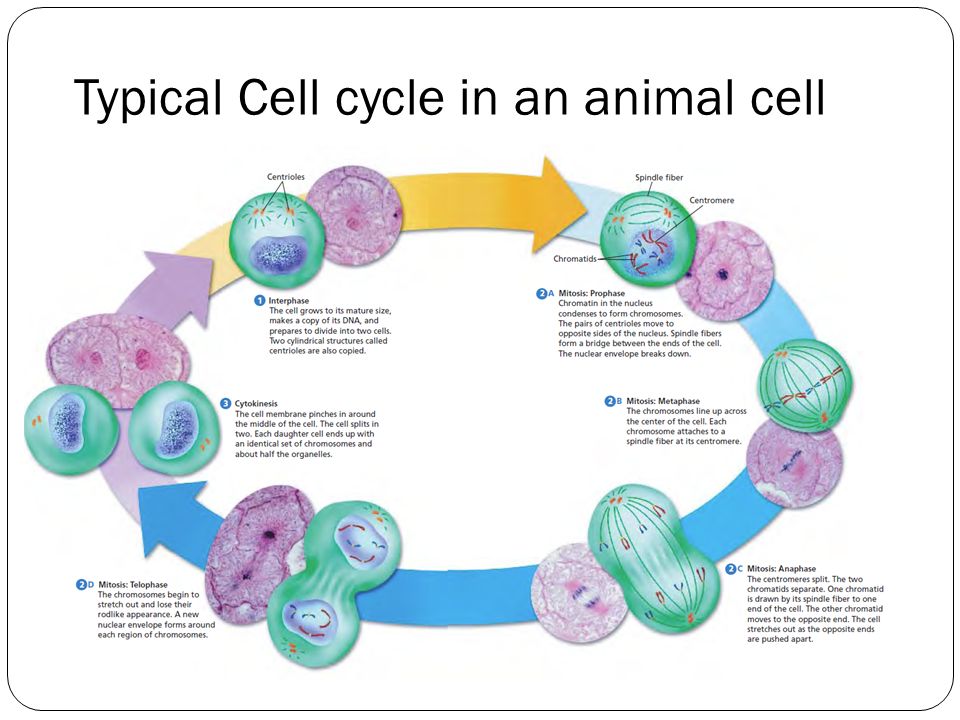
The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells. Figure 2: Animal cell What is the cell cycle. Its stages are described in order along with the parts, regulation, life cycle & purpose. The cell cycle is explained with pictures. Cytokinesis is the shortest phase of the cell cycle that occurs differently in plants and animals. The division in plant cells occurs by forming a cell plate structure in the middle of cell cycle, the ordered sequence of events that occur in a cell in preparation for cell division.The cell cycle is a four-stage process in which the cell increases in size (gap 1, or G1, stage), copies its DNA (synthesis, or S, stage), prepares to divide (gap 2, or G2, stage), and divides (mitosis, or M, stage).The stages G1, S, and G2 make up interphase, which accounts for the span between

8.3: The Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams
The cell cycle is the series of events that occur in a cell leading to its division. It consists of interphase and mitotic phase. Predators hunt to sustain themselves, while prey animals evolve strategies to avoid being caught. This interaction influences population sizes, behaviors, and physical traits of species. Understanding this

The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA replication, and division that produces two identical (clone) cells. In animal cells, a ring The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA replication, and division that produces two identical (clone) cells. In animal cells, a ring