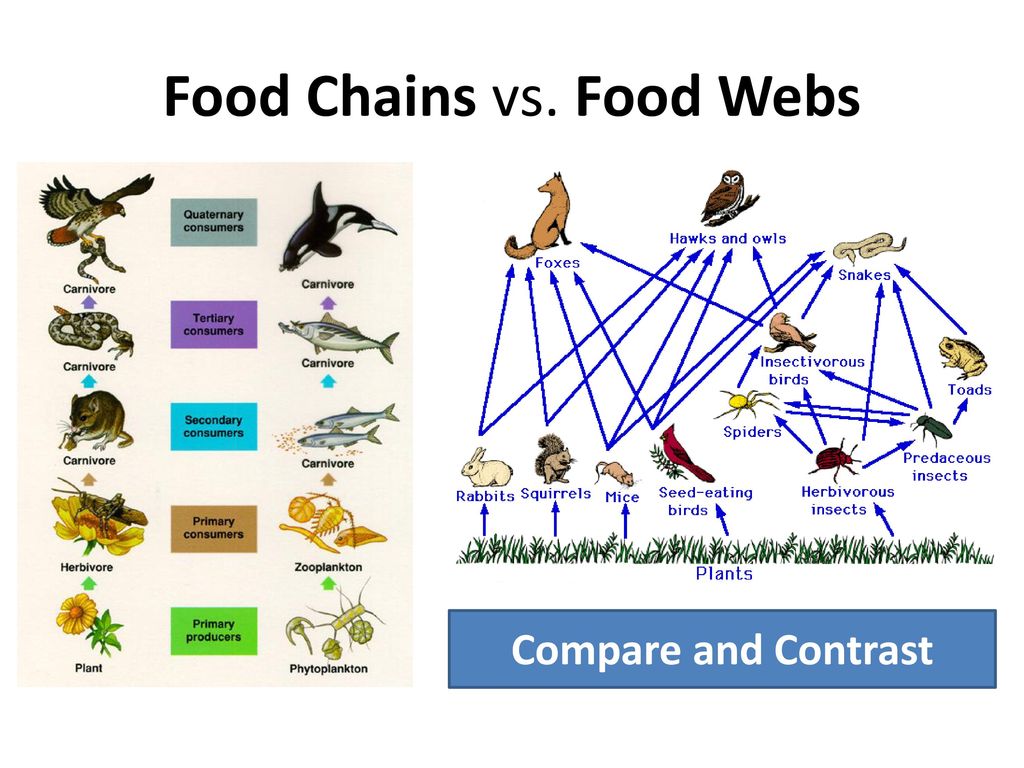
SOLUTION Difference between food chain and food web Biology Diagrams Food chains and webs are vital for supporting biodiversity. By providing multiple energy sources, they enable various species to thrive. In a food chain, each link represents a specific role in an ecosystem, with organisms like plants, herbivores, and predators relying on one another for survival. If one species declines, it can affect others

Summarizing Food chain vs. Food web. All living beings need energy, be it direct or indirect. A food chain shows the energy transmission among different organisms, whereas the food web is a natural linking of who eats what. However, the food web is more practical and, thus, more complex. The food chain is a simplified version of it. Learn the difference between food chain and food web, two ways of representing the energy flow in ecosystems. Compare the number of trophic levels, links, and organisms in each, and how they affect adaptability and competitiveness.

Difference Between Food Chain and Food Web Biology Diagrams
Learn the difference between food chain and food web, two concepts in ecology that describe the flow of energy and nutrients in an ecosystem. A food chain is a linear pathway of organisms, while a food web is a network of interconnected food chains. Learn how food chains and food webs show the movement of energy through an ecosystem. A food chain follows a linear path of energy from producers to consumers, while a food web shows the interconnected paths and trophic levels. Learn the difference between food chain and food web, two ways of representing the flow of energy and nutrients through ecosystems. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms, while a food web is a web-like network of interconnected food chains.

Learn how food chains and webs show the flow of energy and matter in ecosystems. Find out the roles of producers, consumers, decomposers, and scavengers in different habitats and biomes. Food Chains. A food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. An example is shown in Figure below. Food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. Most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. This food chain includes producers and consumers. A food web is a complex arrangement of multiple food chains, providing a more realistic overview of an ecosystem. The difference between the food chain and the food web lies in their simplicity (linear vs. interconnected pathways) and their representation of real-world ecological interactions.