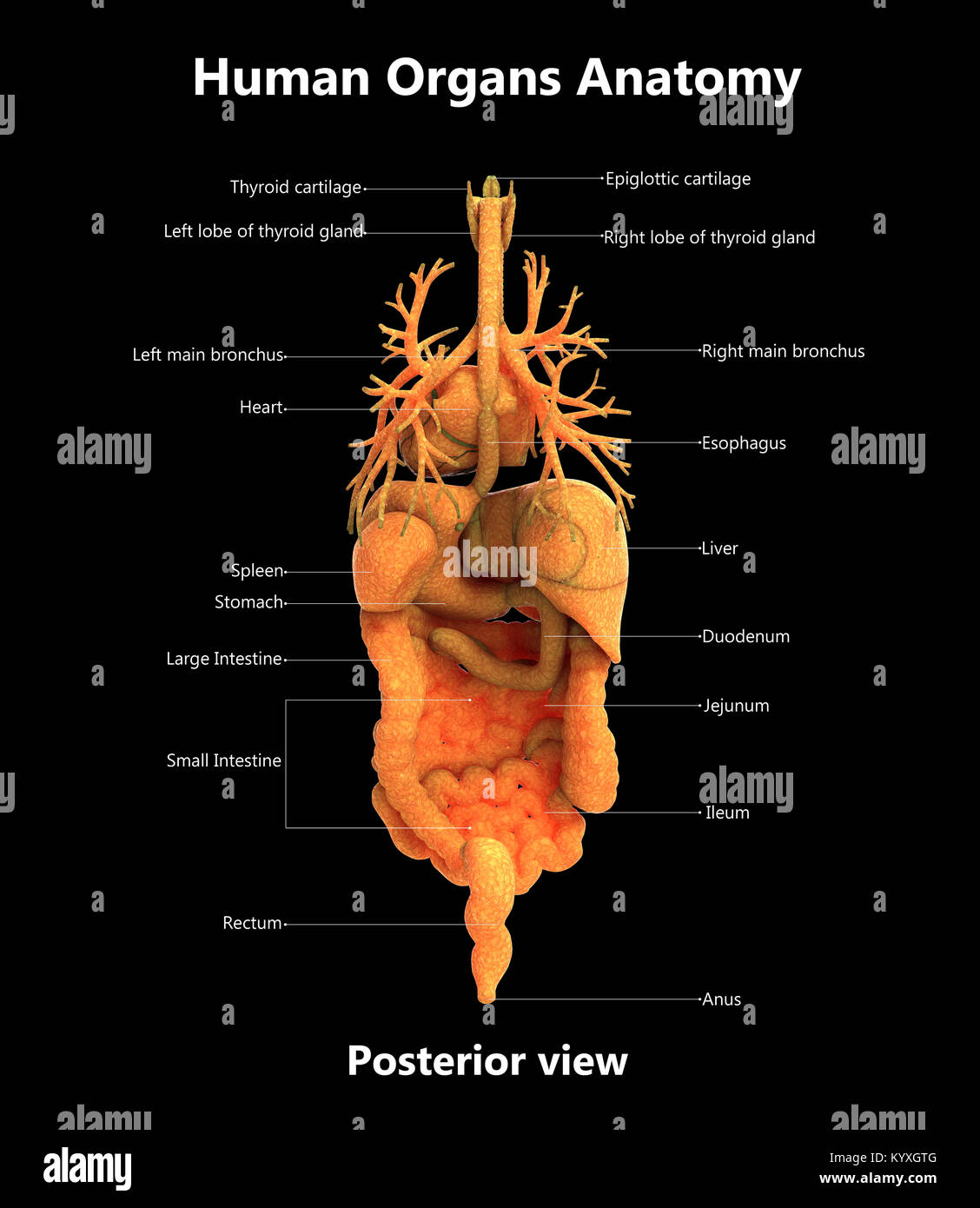
Solved a Anterior viewb Posterior viewb Posterior Biology Diagrams A feature that is posterior to another is closer to the back of the body when the body is in anatomical position. Ventral/Dorsal-Equivalent to belly-side and back-side of a body in anatomical position. For a human in anatomical position, this pair of terms is equivalent to anterior and posterior. The anterior view is the front of the body, and the posterior view is the back of the body. See an illustration of the standard anatomical position of a human body in both anterior and posterior views in Figure 2.7. [1] Figure 2.7 Standardized Anatomical View of the Human Body in (a) Anterior View and (b) Posterior View Human body; Anatomy; Sense organs; Food & kitchen; House; Clothing & articles Sports & games; Your feedback Help. HOME:: HUMAN BEING:: HUMAN BODY:: MAN:: POSTERIOR VIEW. posterior view. previous. next. neck Portion of the body connecting the head to the trunk; the respiratory tract, nerve centers and blood vessels, in particular, pass
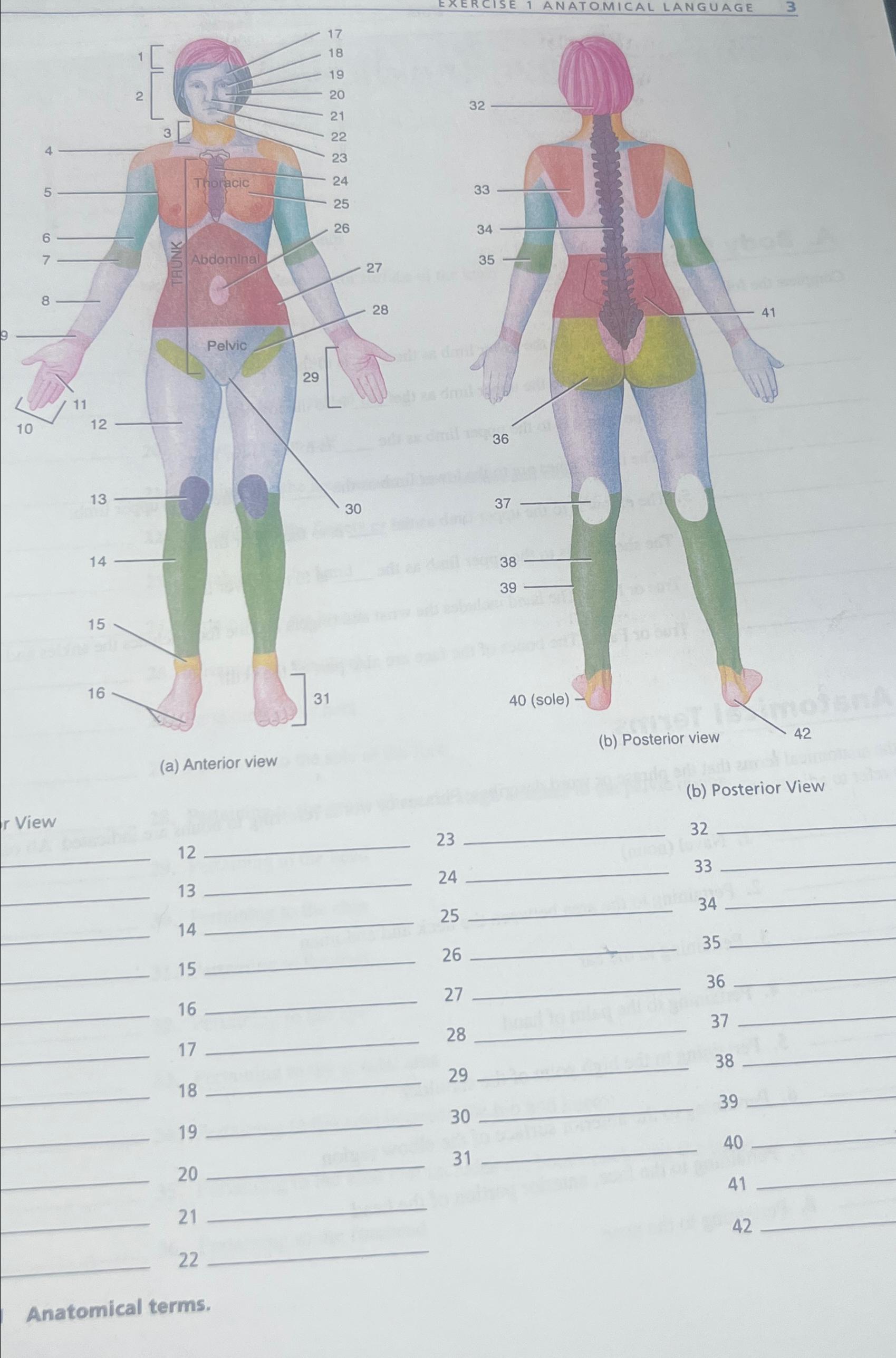
This anatomical diagram presents a clear, back-view illustration of the human skeletal system, highlighting 12 crucial bones and bone groups. The simple red-line drawing effectively demonstrates the basic framework of human anatomy, making it an excellent educational resource for students, healthcare professionals, and anyone interested in understanding human anatomy. Describe the human body using directional and regional terms; Identify three planes most commonly used in the study of anatomy; 1.4.1 - Regions of the Human Body: The human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior view. The regions of the body are labeled in boldface.
Anterior vs. Posterior in Anatomy Biology Diagrams
HOME:: HUMAN BEING:: ANATOMY:: SKELETON:: POSTERIOR VIEW. posterior view. previous. next. parietal bone Flat cranial bone articulating with the frontal, occipital, temporal and sphenoid bones; the two parietal bones form the largest portion of the dome of the skull. Pointy protuberance of the posterior scapula that extends through the acromion. The anterior view is the front of the body, and the posterior view is the back of the body. See an illustration of the standard anatomical position of a human body in both anterior and posterior views in Figure 2.7. [1] Figure 2.7 Standardized Anatomical View of the Human Body in (a) Anterior View and (b) Posterior View Anterior vs. Posterior in Human Anatomy. To better understand the role of "anterior," it helps to compare it to its opposite: posterior. For instance, an anterior-posterior X-ray view means the X-ray beam passes from the front (anterior) to the back (posterior) of the body.