Solved system of many connected food chains in an ecosystem a diagram Biology Diagrams The feeding interactions represented by the food web may have profound effects on species richness of community, and ecosystem productivity and stability (Ricklefs 2008). Types of Food Webs
By studying food chains, ecologists better understand ecosystem dynamics, including the flow of energy, population control, and the impact of human activities on natural habitats. Key Points. Food chains are linear models that illustrate energy transfer from producers to top consumers. Each organism in a food chain contributes to ecosystem balance. In other words, the linear model of ecosystems, the food chain, is not completely descriptive of ecosystem structure. A holistic model—which accounts for all the interactions between different species and their complex interconnected relationships with each other and with the environment—is a more accurate and descriptive model for ecosystems. Food web interactions. Although depictions of food webs often show direct single-line paths of consumption from producers to consumers on various trophic levels like food chains do, they can also show the ways in which some organisms diverge from these patterns. For example, larger carnivores and omnivores whose diets are not limited to a few types of animals may also eat primary consumers if
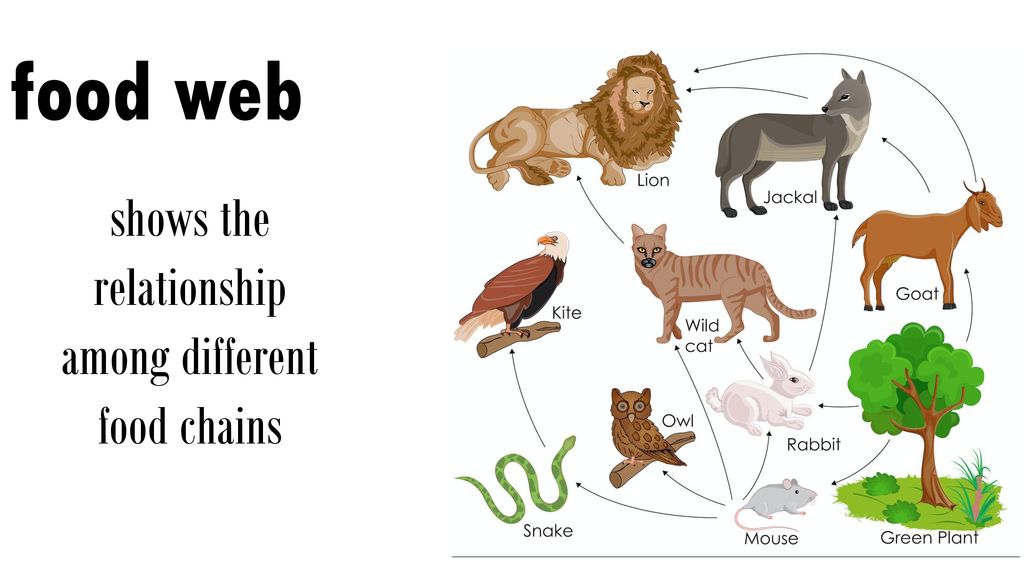
Understanding the Intricacies of a Food Web: An In Biology Diagrams
Food chains and ecosystems have a close relationship. The ecosystem contains all the interactions and energy exchanges, living and non-living, within a region. The food chain is how that energy moves within an ecosystem. Producers create energy, and consumers feed on the producers.

Keeping these points in view, the present chapter has been prepared to give an understanding of species, food chains/webs, and ecosystem. Discover the world's research 25+ million members

Definition, Examples, Types Biology Diagrams
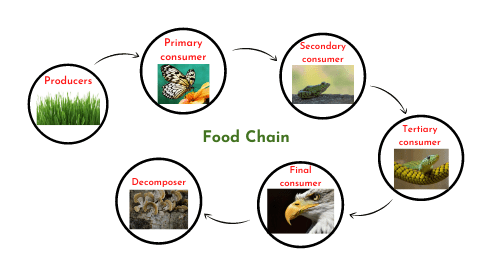
A food chain is a linear sequence that shows how energy flows from one organism to another, starting from a primary producer and culminating in apex consumers. change or habitat destruction. By probing the complexities of food webs, scientists can identify key species and interactions that maintain ecosystem functionality, guiding