The Great Barrier Reef Biology Diagrams Learn how coral reefs, the largest and most diverse ecosystems on Earth, are interconnected by a complex food web. Discover the roles of producers, consumers, and predators in the Great Barrier Reef and other coral reefs.
The ecosystem of the Great Barrier Reef is a fragile balance, with a food chain that has several points, in which each one is reliant on one another. The Great Barrier Reef's coordinates are 18.2871° S, 147.6992° E. The Reef has a huge amount of flora …show more content… On the Great Barrier Reef, there is a symbiosis environment with many fishes and organisms relying on each other for food and protection. In this underwater video, researcher Richard Fitzpatrick explains some of the various fishes and how they prey and avoid being prey for other creatures. Learn how energy and nutrients flow through a coral reef ecosystem, and the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposers. Explore the trophic levels, food chains, and food web of the Great Barrier Reef with illustrations and questions.

Great Barrier Reef Food Web: Unveiling the Marine Ecosystem Biology Diagrams
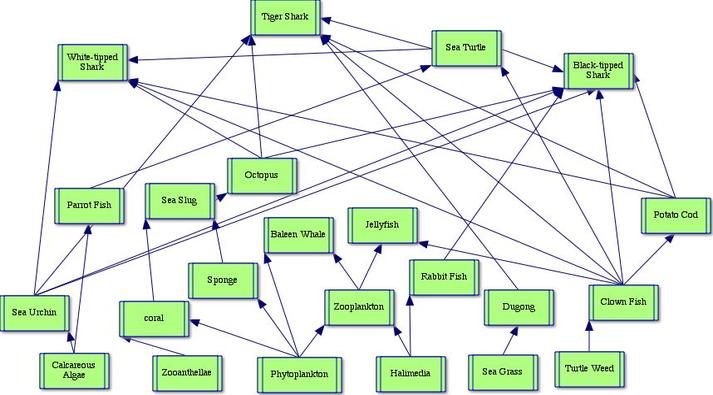
This is a Coral Reef Food Web.See if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. Look for: The Producers - the phytoplankton on the ocean's surface.. The Primary Consumers - the coral, sea turtle, and fish.. The Secondary Consumers - the sharks, anemones, starfish, baracuda, jellyfish, sea snakes and sea slugs. A food web consists of all the food chains in a single ecosystem.Each living thing in an ecosystem is part of multiple food chains. Each food chain is one possible path that energy and nutrients may take as they move through the ecosystem. Not all energy is transferred from one trophic level to another. Energy is used by organisms at each trophic level, meaning that only part of the energy For example, a food chain in the Great Barrier Reef might include phytoplankton as the producer, shrimp as a primary consumer, a squid as a secondary consumer, and a shark as a tertiary consumer.

Large reef fish, sharks, eels and barracudas make up the tertiary consumers at the top of the food chain. Marine mammals such as dolphins and seals, as well as sea birds, also act as tertiary consumers. The Great Barrier Reef is home to over 1,500 species of fish, 4,000 species of mollusks and over 200 species of birds.

PDF Coral Reef Food Web Biology Diagrams
Learn how the marine creatures of the reef are interconnected in a complex food chain with multiple levels. See a diagram of the food web and discover the threats to its balance and survival. The Structure and Components of the Great Barrier Reef Food Web. The Great Barrier Reef, known for its stunning reefs and crystal-clear water, is home to a complex and fascinating food web. This intricate network of interconnected organisms, including fish, corals, and other marine life, relies on each other for survival.

