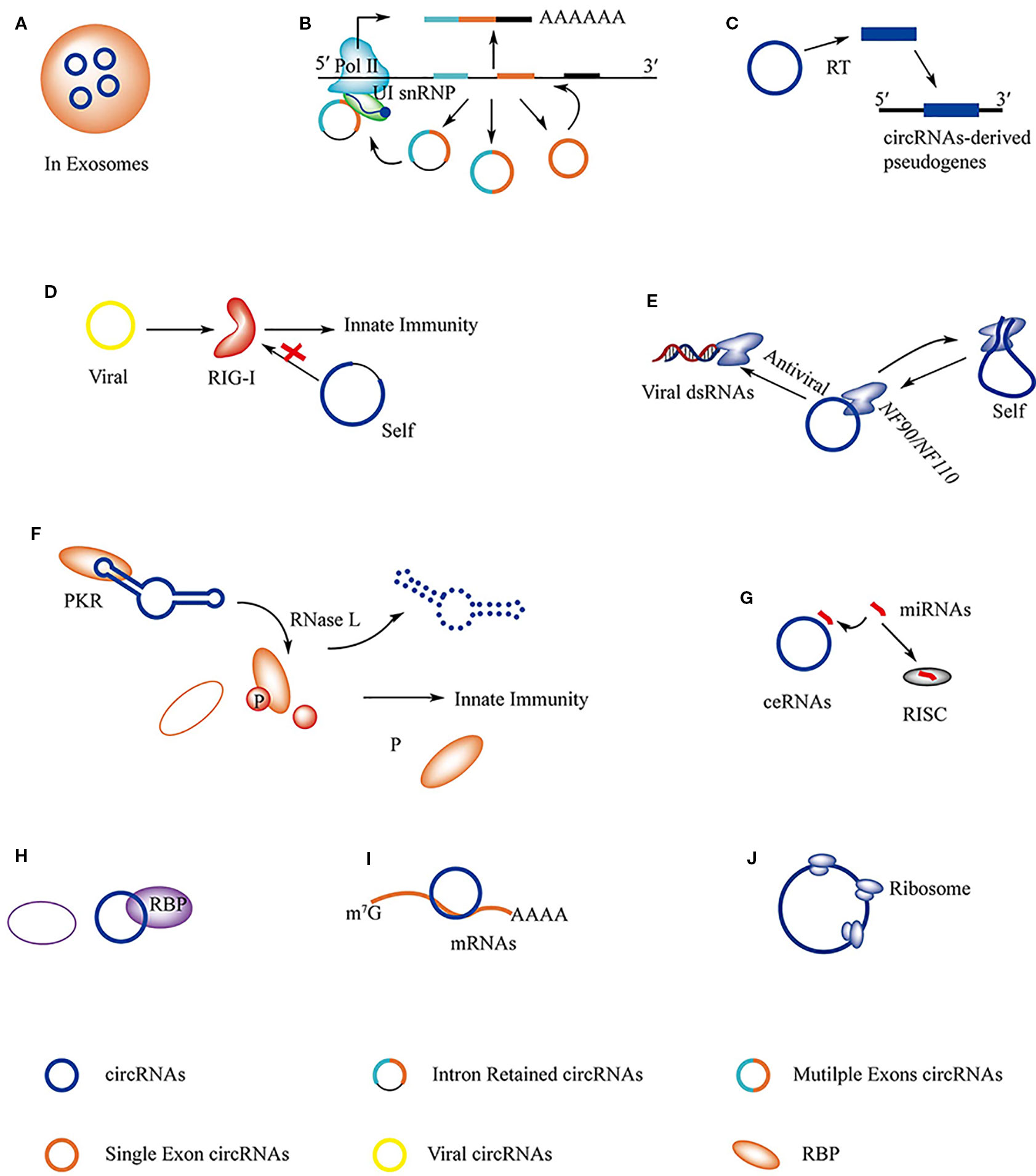
The Role of NonCoding RNAs in Controlling Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams The mammalian cell cycle is precisely controlled by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and related pathways such as the RB and p53 pathways. Recent research on long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) indicates that many lncRNAs are involved in the regulation of critical cell cycle regulators such as the cyclins, CDKs, CDK inhibitors, pRB, and p53. Another ncRNA, lincEnc1 (ref. 25), was predicted to have a role in cell-cycle regulation in embryonic stem (ES) cells and has been shown in a separate study to affect the proliferation of ES cells 68. Circular RNAs (circRNAs), a type of non‐coding RNA, are single‐stranded circularized molecules characterized by high abundance, evolutionary conservation and cell development‐ and tissue‐specific expression. The functions and mechanisms of circRNAs in cell cycle regulation are largely focused on the G 1/ S phase transition and
These results indicate that lncRNAs that have cell-cycle-specific expression are candidates for regulation of cell-cycle progression and that they have distinct functions. There are a large number of these RNAs, each expressed at a specific time in the S-phase, which might facilitate the maintenance of gene expression programs in human cells.
Cell cycle regulation by long non Biology Diagrams
Holdt, L. M. et al. Alu elements in ANRIL non-coding RNA at chromosome 9p21 modulate atherogenic cell functions through trans-regulation of gene networks. PLoS Genet. 9 , e1003588 (2013).

MINCR exerted inhibitory effects on the cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of NSCLC cells by activating c-Myc and its downstream effectors, suggesting that this lncRNA could be used as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of NSCLC. Roles of MYC-targeting long non-coding RNA MINCR in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis in non-small Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions there have been ~50,000 publications with 'long non-coding RNA' as a key term and more than 2,000 cell cycle and Cyclins and CDKs are key players in cell cycle regulation (Fig. 1). NcRNA CCND1, also called pncRNA (promoter-associated non-coding RNA), is transcribed from the upstream region of the cyclin D1 gene, CCND1, and negatively regulates cyclin D1. NcRNA CCND1 functions as a transcription factor regulator .

