Vagus nerve labeled and human organs medically Biology Diagrams The vagus nerve, or the 10th cranial nerve (CN X), is primarily associated with the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, however, it also has some sympathetic influence through peripheral chemoreceptors.The vagus nerve is a mixed nerve, as it contains both afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) fibers.This means it is responsible for not only carrying motor signals to the 1. Intracranial course. The vagus nerve exits the cranial cavity through the jugular foramen in the posterior cranial fossa. At the jugular foramen, the nerve contains two sensory ganglia: a-The superior ganglion (jugular ganglion), related to somatic sensation. b-The inferior ganglion (nodose ganglion), associated with visceral sensation and taste.
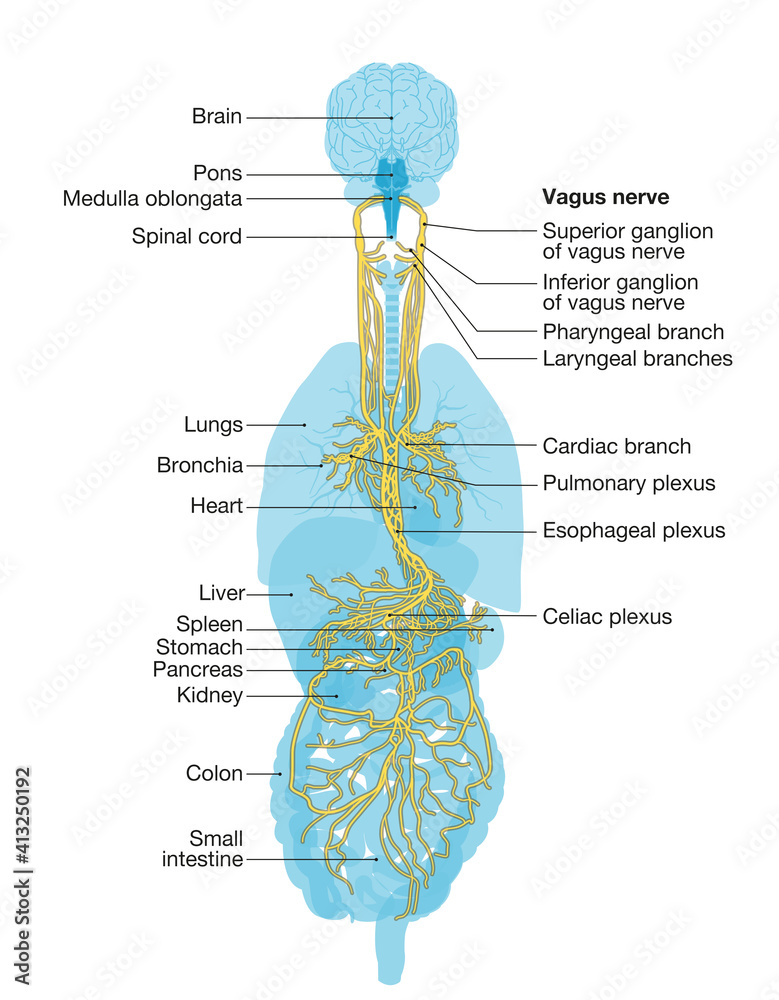
The longest cranial nerve, it splits into the anterior vagus nerve and the posterior vagus nerve. Swallowing and speaking are governed in part by the anterior vagus nerve, which provides innervation to the pharynx, larynx, and oesophagus. The posterior vagus nerve controls digestion, heart rate, and blood pressure in addition to innervating the heart and lungs.The vagus nerve is The vagus nerve controls many critical functions of the human body, and for this reason, medical science is seeking ways to modulate its actions. This article looks at the anatomy and function of the vagus nerve as well as medical conditions that can affect it. It also explores the effectiveness of vagus nerve stimulation and where the The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), is one of the most complex and multifunctional nerves in the body. The Human Brain: An Introduction to Its Functional Anatomy (7th ed.). Elsevier. ISBN 978-0323653985. Williams, P. L., & Warwick, R. (2020). Gray's Anatomy (40th ed.). Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0443071683
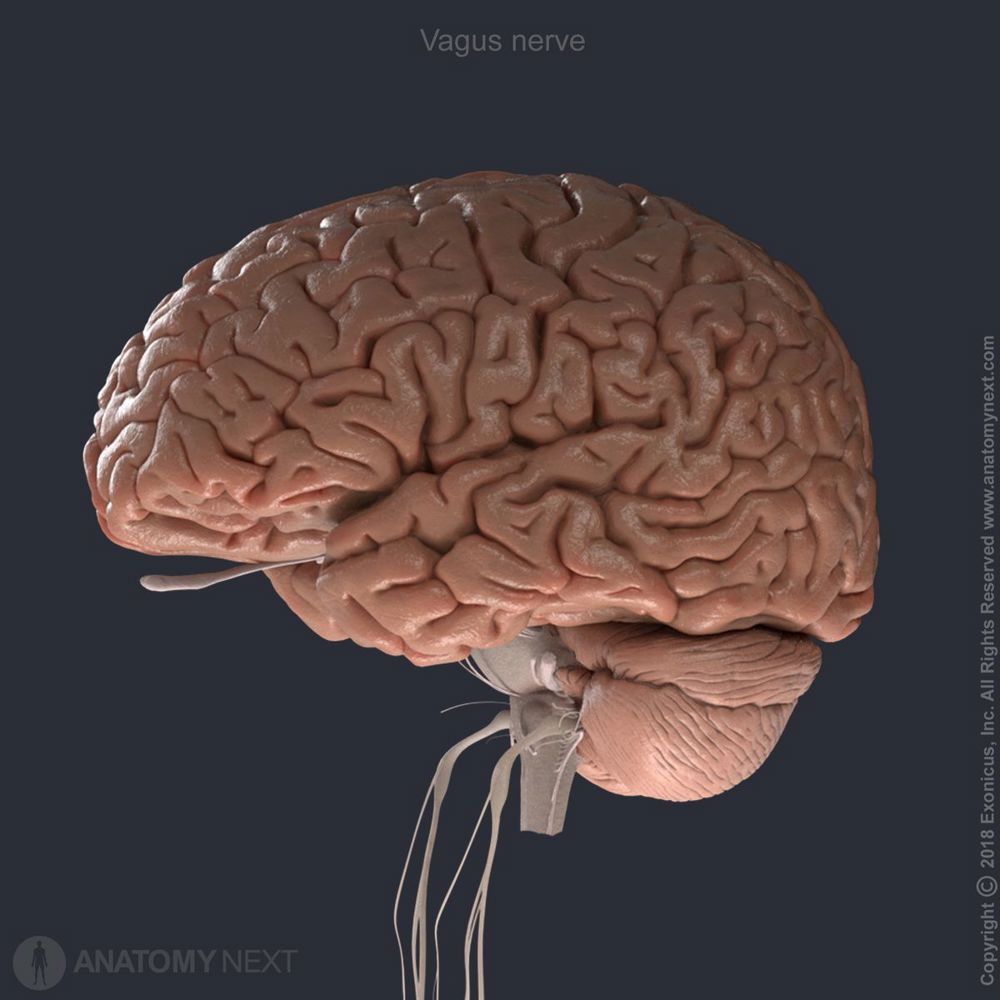
Structure, Location, Function, Anatomy, Diagram Biology Diagrams
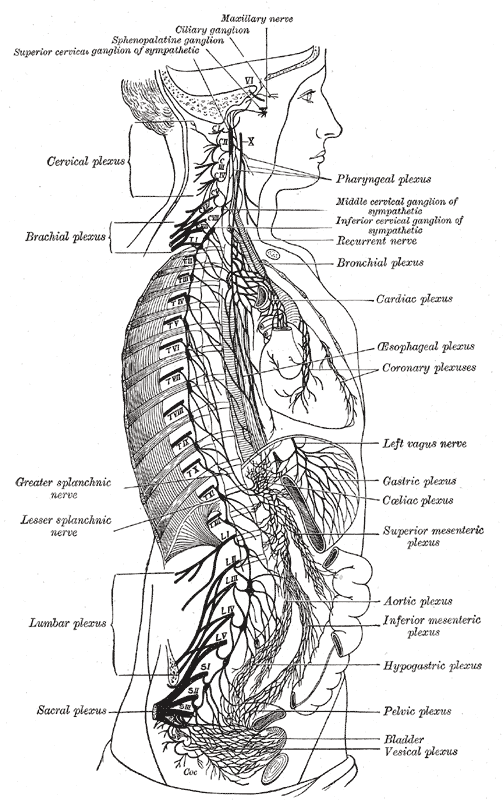
The vagus nerve (cranial nerve [CN] X) is the longest in the body, containing both motor and sensory functions in afferent and efferent regards. The nerve travels widely throughout the body, affecting several organ systems and regions of the body, such as the tongue, pharynx, heart, and gastrointestinal system. Because of the wide distribution of the nerve throughout the body, there are The vagus nerve (/ ˈ v eɪ. ɡ ə s /), also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that carries sensory and motor fibers. It creates a pathway that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. [1]It comprises two nerves: the right and the left vagus nerve. In the neck, each nerve contains about 105,000

The vagus nerve is the 10 th cranial nerve (CN X). It is a functionally diverse nerve, offering many different modalities of innervation. It is associated with the derivatives of the fourth and sixth pharyngeal arches. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the vagus nerve - its anatomical course, functions and clinical correlations.

Vagus Nerve Anatomy: Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic ... Biology Diagrams
The vagus nerve plays a crucial role in the human body, connecting the brain to various organs and systems. Anatomy of the Vagus Nerve. The vagus nerve consists of both sensory and motor fibers, making it a mixed nerve. It emerges from the brainstem and divides into two main branches, the left and right vagus nerves. These branches then
The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve. It contains motor and sensory fibers and, because it passes through the neck and thorax to the abdomen, has the widest distribution in the body. Sanders I, Mu L. Anatomy of the human internal superior laryngeal nerve. Anat Rec. 1998 Dec. 252(4):646-56. [QxMD MEDLINE Link]. Sasaki CT, Isaacson G