worksheet from EdPlace Biology Diagrams Think about it, a single strawberry that weighs 12g (on average) is already one-sixth of a rabbit's daily food intake. Wild rabbits are not going to need much from you to be able to keep up their daily calories. Instead, wild rabbits will be able to consume most of their necessary food as grass and leafy plants. A significant link in the food chain is the rabbit. It is a tiny mammal that is widespread around the globe. As herbivores, rabbits consume only plants and other flora for food. For many predators, such as foxes, coyotes, and raptors, they are a significant source of food. Skunks and raccoons, among other scavengers, can also find food in rabbits. We will also discuss the relationship between rabbits and predators, the role of rabbits in the food chain, and the population dynamics of rabbits. The Role of Rabbits in Ecosystems. Rabbits play a significant role in many ecosystems as they are herbivorous animals that feed on vegetation. They help to control the plant population by eating the

Wild Rabbit Ecology: Food Web, Lifespan, Habitat, Eating Habits Food web and foraging behavior. Rabbits are near the bottom of the food chain in the wild. For this reason, they live for a year or two, even though domestic rabbits often live close to ten years. When wild rabbits graze, they need constant alertness for predators.
What Do Wild Rabbits Eat? A Diet of the Obvious and the Odd Biology Diagrams
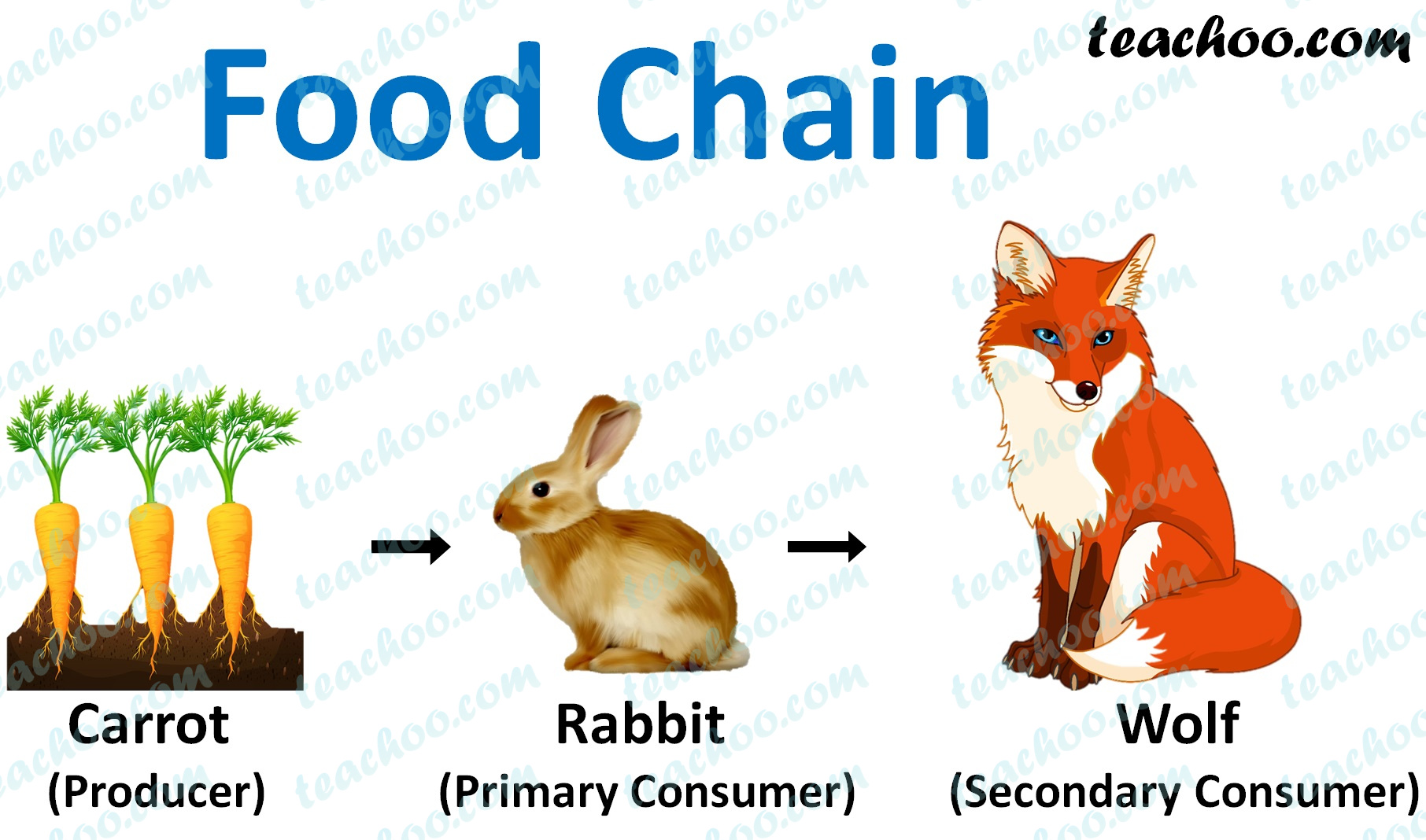
A rabbit food chain shows how energy is passed from one organism to another. Rabbits are a significant part of the food chain and keep the ecosystem balanced. Wild rabbits like the Eastern Cottontail don't eat rabbit food like domestic rabbits. They eat food such as: Twigs; Grass; Young plant shoots; Dandelions; Bark; Hay; Domestic Rabbits. Wild rabbits draw their genesis from Europe & Africa. Explore what do wild rabbits eat in the wild, types of wild rabbits & their diets, and predators here. Rabbits are essential to the animal food chain because they are a significant food source to a wide array of animals, which include owls, hawks, and foxes. Cite This Page. APA7 MLA8 Explore the unique dietary habits of wild rabbits; from their reliance on natural food sources to seasonal adaptations. This article delves into what wild rabbits eat, analyzing food selection based on nutritional value and availability, and discussing the risks and benefits of foraging. It also draws an enlightening comparison between the diets of wild and domestic rabbits, emphasizing the

A rabbit is a member of the order Lagomorpha, which also includes pikas and hares. Rabbits are herbivores, meaning that they eat plants. As primary consumers, rabbits play an important role in the food chain by converting plant material into energy that can be used by other organisms. They are preyed upon by a variety of predators, including foxes, owls, and snakes. Rabbits are social animals Given rabbits' position in the food chain, they're prone to attacks from numerous predators like foxes, hawks, owls, and even domestic dogs and cats. To maximize their survival, wild rabbits incorporate diverse safety measures during their food search. Selective feeding sites are one such protective measure. Rabbits are herbivorous grazers, meaning their diet primarily consists of plant material. In the wild, rabbits feed on a variety of vegetation such as grass, weeds, leaves, and bark. The Rabbit's Key Role in the Ecosystem Food Chain. Rabbits play a crucial role in the food chain within the ecosystem. As prey animals, they serve as a vital

